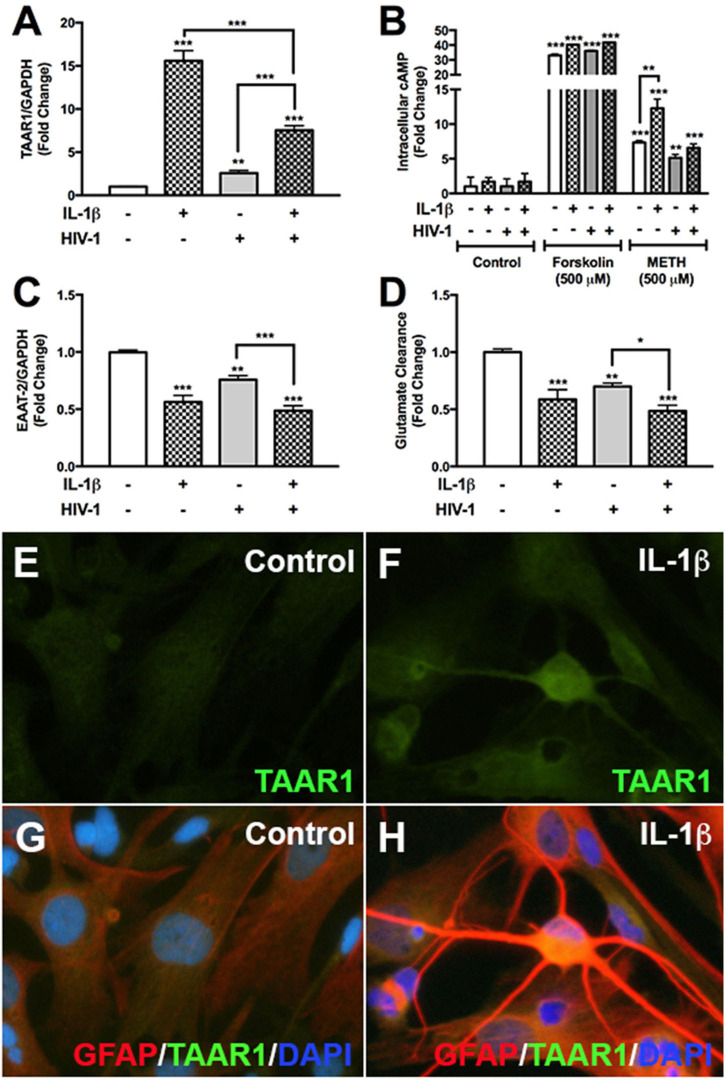
Figure 1.
HIV-1 and IL-1β regulate astrocyte TAAR1 & EAAT-2 mRNA levels and function. Primary human astrocytes were treated with HIV-1 (p24 10 ng/mL, gray bars) and IL-1β (20 ng/mL, hatched bars) alone or in combination, and untreated astrocytes were maintained in parallel. TAAR1 mRNA levels were analyzed following treatment with IL-1β ± HIV-1 (A). Intracellular cAMP was quantified to evaluate TAAR1 signaling subsequent to IL-1β ± HIV-1 pretreatment and following 15 min of forskolin or METH stimulation and represented as fold change to control (B). EAAT-2 mRNA levels were evaluated following IL-1β ± HIV-1 treatment (C). Glutamate clearance was measured at 10 h post-glutamate addition (D). Control and IL-1β pretreated cells were fixed and immunostained for glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP, red), TAAR1 (green) and DAPI (blue) (E–H). Statistical analyses were performed using GraphPad Prism V6.0 with One-way ANOVA and Tukey's post-test for multiple comparisons. P ≤ 0.05 were considered statistically significant and data represent means ± SEM. Representative donors were chosen from a minimum of three astrocyte donors each tested and analyzed in a minimum of triplicate determinations (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001).