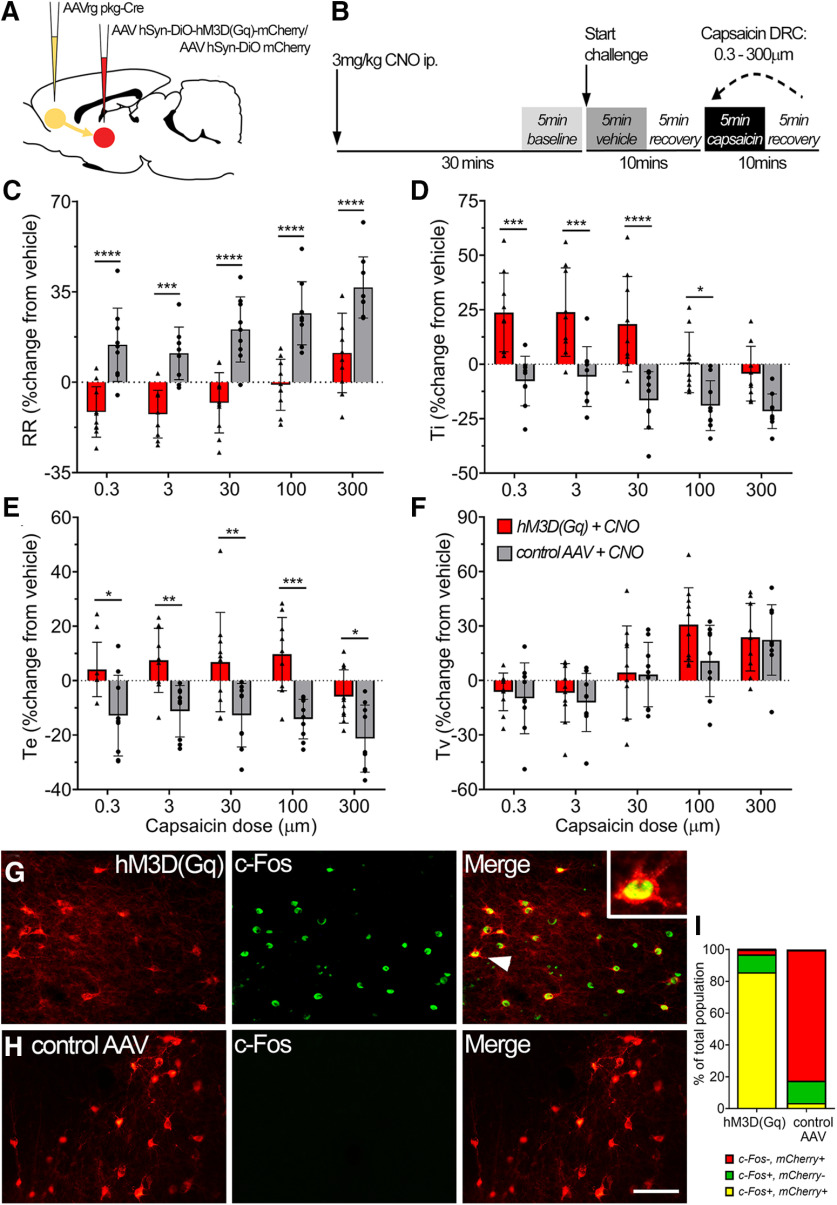
Figure 5.
Activation of the SubM–VLO circuit in conscious unrestrained rats regulates nocifensive respiratory reflexes induced by inhalation of capsaicin. A, Microinjection of AAVrg pkg-Cre into the VLO to achieve Cre-dependent expression of either hM3D(Gq) mCherry or control mCherry in SubM–VLO projecting neurons only. B, Schematic outlining the conscious respiratory challenge protocol. C–F, Respiratory parameters measured during conscious capsaicin challenge in hM3D(Gq) + CNO (N = 10) or control AAV + CNO (N = 9) rats: respiratory rate (RR; C), inspiratory time (Ti; D), expiratory time (Te; E), Tidal volume (Tv; F). G, H, Representative images of c-Fos (green) expression in SubM neurons expressing either hM3D(Gq) mCherry (G) or control AAV mCherry (H) following administration of CNO 2 h before rats were killed. Arrowhead indicates colabeled neuron in box insert. I, Quantification of the number of SubM neurons expressing mCherry and/or c-Fos represented as a percentage of the total number of mCherry and/or c-Fos neurons counted [hM3D(Gq), 529 neurons; control AAV, 580 neurons]. *p < 0.05; **p < 0.01; ***p < 0.001; ****p < 0.0001, hM3D(Gq) versus control AAV by Bonferroni's multiple comparisons (C–F). Scale bars: G, H, 75 µm.