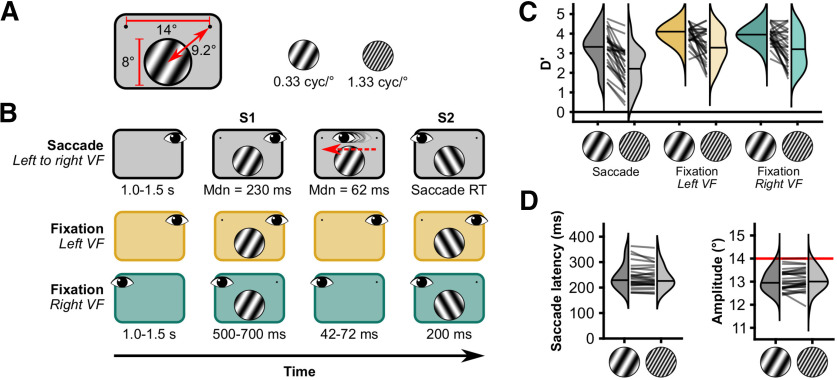
Figure 1.
Stimuli, experimental paradigm and behavioral results. A, Stimuli were sinusoidal gratings (diameter, 8°) presented 9.2° from a fixation point to the upper left or right of the grating. The spatial frequency was either 0.33 cycle/° or 1.33 cycles/°. B, Trial timeline. Subjects completed three conditions of an orientation change detection task. In each condition, the task was to indicate whether the orientation changed from S1 to S2. The change in orientation was always 60° and occurred on half of the trials. In Saccade trials, saccades were always made from right to left, and the orientation could be changed during the saccade. In Fixation trials, a blank period of 42–72 ms was presented between S1 and S2. Saccade and Fixation trials were presented in separate blocks. Left and right fixation trials were randomly interleaved. C, Change detection performance. Lines represent individual subjects. Horizontal lines in distribution patches represent median D′. D, Oculomotor performance. cyc, Cycles; Mdn, median.