Figure 3.
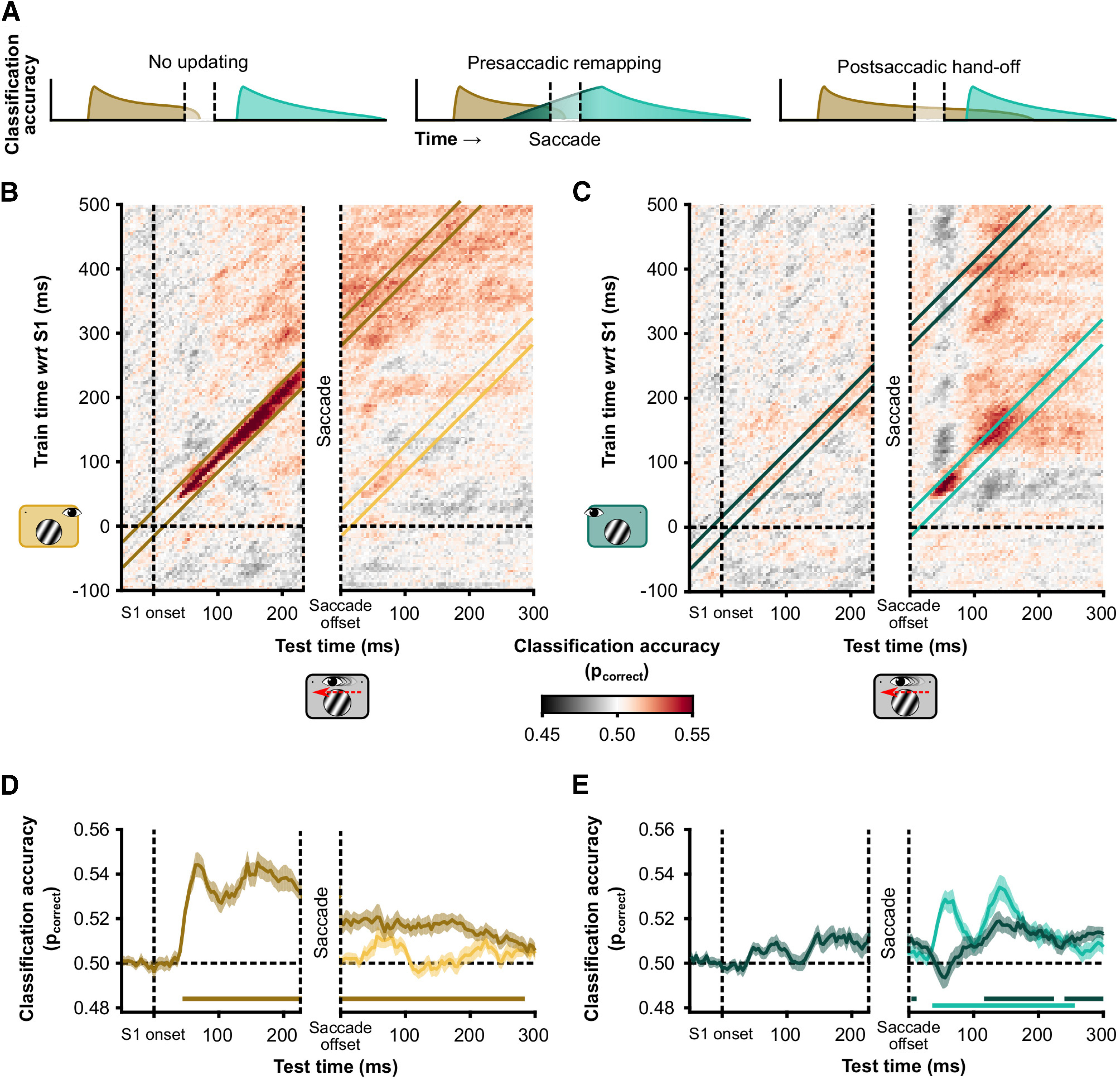
Temporal generalization of cross-decoding. A, Hypothetical decoding of spatial frequency across saccades. Brown represents classification accuracy of a classifier trained on data from the Fix-LVF condition (i.e., the presaccadic classifier). Cyan represents classification accuracy of a classifier trained on data from the Fix-RVF condition (i.e., the postsaccadic classifier). We consider three hypotheses. First, spatial frequency information is not updated and is available only in retinotopic conditions (no updating). Second, the postsaccadic classifier can classify spatial frequency before saccade onset, and therefore before the stimulus location in the train data is retinotopically matched to the test data (presaccadic remapping). Third, the presaccadic classifier can classify spatial frequency well into the postsaccadic window (soft handoff). B, Classifiers were trained using the Fix-LVF data, corresponding to the presaccadic visual field in the Sac-LVF condition. The Sac-LVF data were used to assess classifier accuracy. The Sac-LVF data were aligned to S1 onset (left side of the generalization matrix) and to saccade offset (right side of the generalization matrix). The width of the presaccadic window is matched to the overall median saccade latency = 226 ms. The width of the saccade window corresponds to the overall median saccade duration = 62 ms. Note that on some trials in the left half of the temporal generalization matrix the saccade had already been executed after 150 ms. Also note that limiting the presaccadic window further to 150 ms after stimulus onset would not change the interpretation. C, Like B, but using as training data the Fixation, right VF condition for the classifier. D, For each participant, we calculated the average classification performance in two diagonal bands (illustrated in B). One diagonal reflects the similarity between S1 evoked responses in the Fix-LVF condition (brown) and the S1 evoked response in the Sac-LVF condition. The other diagonal (yellow) represents the similarity between the S1 evoked response in the Fix-LVF condition and the saccade offset evoked response in the Sac-LVF condition. Lines represent the group average (N = 28); the shaded area represents 1 SEM across subjects. Statistical significance, indicated by the horizontal colored lines, against chance level was assessed with one-sample t tests on the log-odds of correct classification, corrected for multiple comparisons using cluster-based permutations with threshold-free cluster enhancement. E, Like D but with the Fix-RVF as training data. Diagonals are illustrated in C.
