Figure 4.
Modulation of the JNK Signaling Pathway in Aβ42-Expressing Clones Dictates the Survival or Elimination of WT Cells
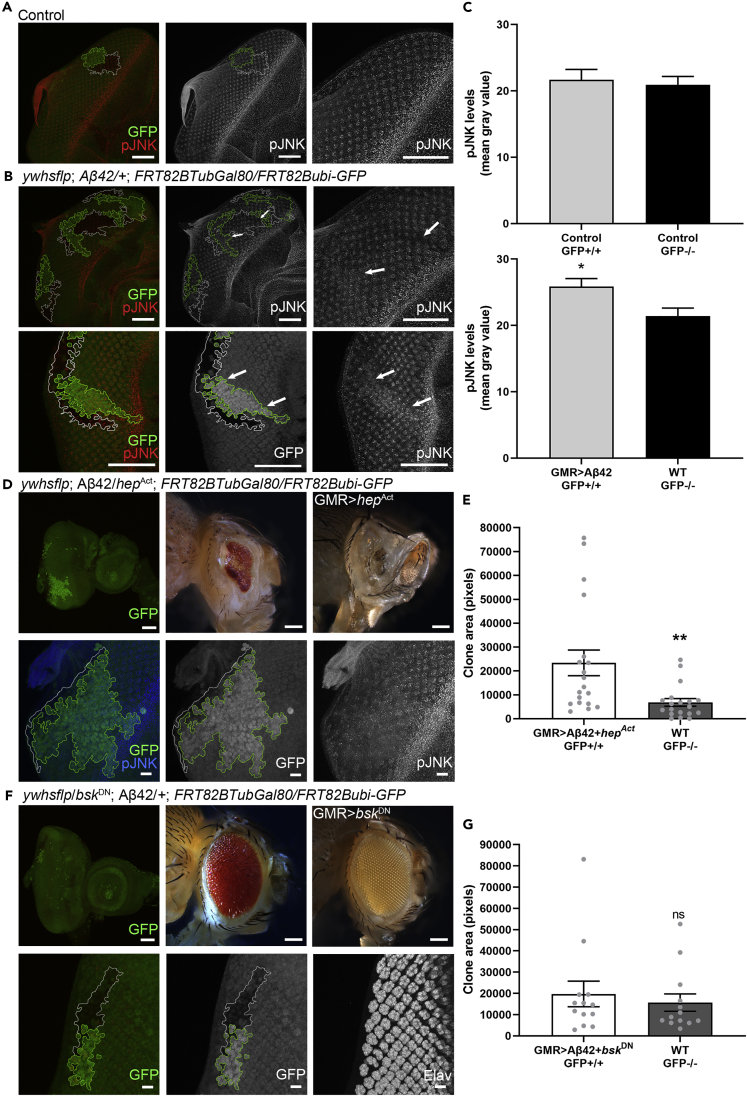
(A) Control clones show a regular pattern of pJNK staining throughout the eye disc. This pattern is consistent across WT GFP-positive and WT GFP-negative clones. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(B) Eye disc with GFP-positive clones expressing Aβ42. pJNK levels are increased in Aβ42-expressing clones. Magnification shows increased pJNK signal overlapping with the Aβ42-expressing clone. The upregulation of pJNK expression in Aβ42-expressing clones extends into WT sister clones. Scale bars, 50 μm.
(C) pJNK levels were compared for control sister clones and Aβ42-expressing and WT sister clones. No significant difference was observed between control clones (N = 17, p = 0.72, two-way unpaired Student's t test). Data are presented as mean ± SEM. We observed an increase in pJNK mean gray value in Aβ42-expressing clones (N = 17, ∗p < 0.05, two-way unpaired Student's t test). Because pJNK staining results in strong signal in the optic stalk, for pJNK mean gray value calculation, we selected for analysis the region of the z stack that did not substantially overlap with the optic stalk staining.
(D) To test the effects of upregulating JNK signaling, we expressed hepAct in Aβ42-expressing cells. Expression of hepAct in clones led to a non-autonomous increase in cell death throughout the entire eye, resulting in highly reduced eyes. Expression of hepAct in all retinal neurons using GMR-Gal4 (GMR > hepAct) triggers neurodegeneration. WT sister clones are highly reduced in size compared with clones expressing Aβ42 and hepAct. Staining for pJNK revealed a region of increased pJNK levels overlapping with the area of the GFP-positive clone.
(E) GFP-positive clones expressing Aβ42 and hepAct and GFP-negative WT clone sizes were quantified. WT sister clones are significantly reduced in size compared with clones expressing Aβ42 and hepAct (N = 19, ∗∗p < 0.01, two-tailed unpaired Student's t test). Data are presented as mean ± SEM.
(F) To test the effects of downregulating JNK activity, we expressed bskDN in Aβ42-expressing neurons. Adult flies expressing bskDN in Aβ42-expressing neuronal clones show approximately WT eye size. Expression of bskDN in all retinal neurons using GMR-Gal4 (GMR > bskDN) results in eyes that are normal in appearance (ywhsflp/bskDN; Aβ42/+; FRT82BTubGal80/FRT82ubi-GFP). Expression of bskDN in Aβ42-expressing cells rescues the size of WT clones. Staining retinal neurons with Elav shows irregular spacing in the Aβ42-expressing clone but normal spacing in the WT clone.
(G) Areas of GFP-positive clones expressing Aβ42 and bskDN were compared with GFP-negative WT sister clones, showing no significant difference in size (N = 13, p = 0.58, two-tailed unpaired Student's t test).
Data are presented as mean ± SEM. See also Figures S1 and S2 and Table S1.