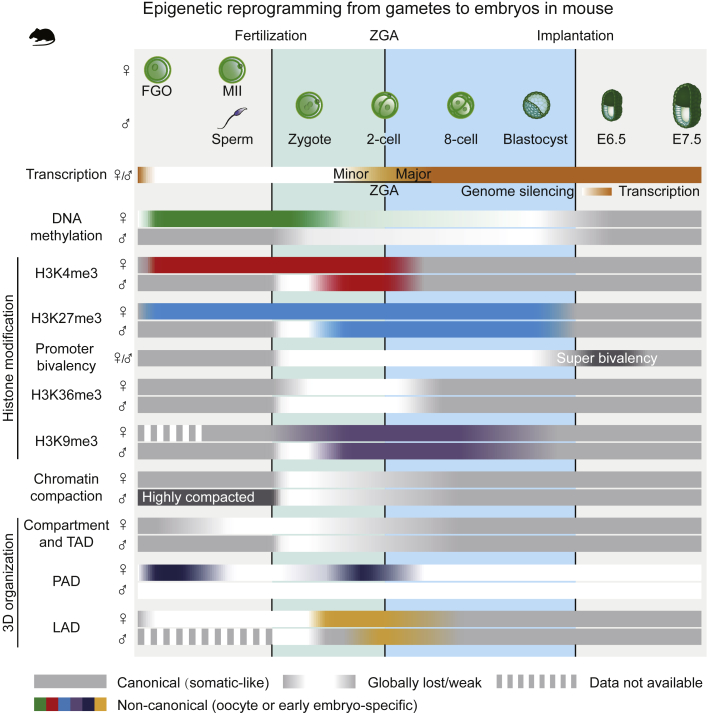
Figure 1.
Epigenetic Reprogramming during the Gamete-to-Embryo Transition in Mouse
In mouse, global genome silencing starts in late-stage gametes and lasts until ZGA in embryos. In oocyte, DNA methylation is established in a transcription-dependent manner. Sperm genome is methylated in both transcribing and non-transcribing regions. After fertilization, DNA methylation undergoes global erasure and re-establishment in post-implantation embryos. While sperm largely exhibits canonical patterns of histone modification, non-canonical patterns of histone modifications are found in oocytes and early embryos. Broad domains of non-canonical H3K4me3 (ncH3K4me3) and H3K27me3 are established in oocytes and can be briefly transmitted into embryos (except promoter H3K27me3). On the paternal allele, sperm H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 are replaced by broad domains of de novo H3K4me3 and H3K27me3 in zygotes after fertilization. While H3K4me3 is reprogrammed to a canonical pattern upon ZGA, H3K27me3 domains can be maintained until blastocyst and reset to a canonical pattern in post-implantation embryos. At promoters of developmental genes, the bivalency (H3K4me3/H3K27me3) is lost in pre-implantation embryos but reappears at E6.5 at unusually strong levels, forming “super-bivalency.” It becomes attenuated again at E7.5. H3K36me3, which marks transcribing gene bodies, is established in gametes, removed after fertilization, and re-established after ZGA in early embryos. H3K9me3 marks LTRs in gametes. After fertilization, H3K9me3 is reset to a transitionary state that persists to blastocyst. Blastocyst-specific H3K9me3 starts to emerge from the 4-cell stage. In post-implantation embryos, H3K9me3 also marks lineage-specific genes. Sperm exhibits canonical compartments A/B and TADs, while oocytes show compartments A/B, TADs, and PADs (a non-canonical chromatin 3D structure) in FGOs and metaphase-like structures in MII oocytes. These structures become globally weakened in early embryos and are then gradually reconsolidated as development proceeds. PADs also briefly reappear in 1-cell stage (weak but detectable) and 2-cell stage. LADs are lost in FGOs but are de novo established starting from the 1-cell embryos. LADs show unique features on the maternal allele in zygotes and on both alleles at the 2-cell stage. Canonical (somatic-like) patterns of epigenomes are marked in gray, while non-canonical (oocyte or early embryo-specific) patterns of epigenomes are marked in colors. FGO, full-grown oocyte; LAD, lamina-associated domain; PAD, Polycomb associating domain; TAD, topological associating domain; ZGA, zygotic genome activation.