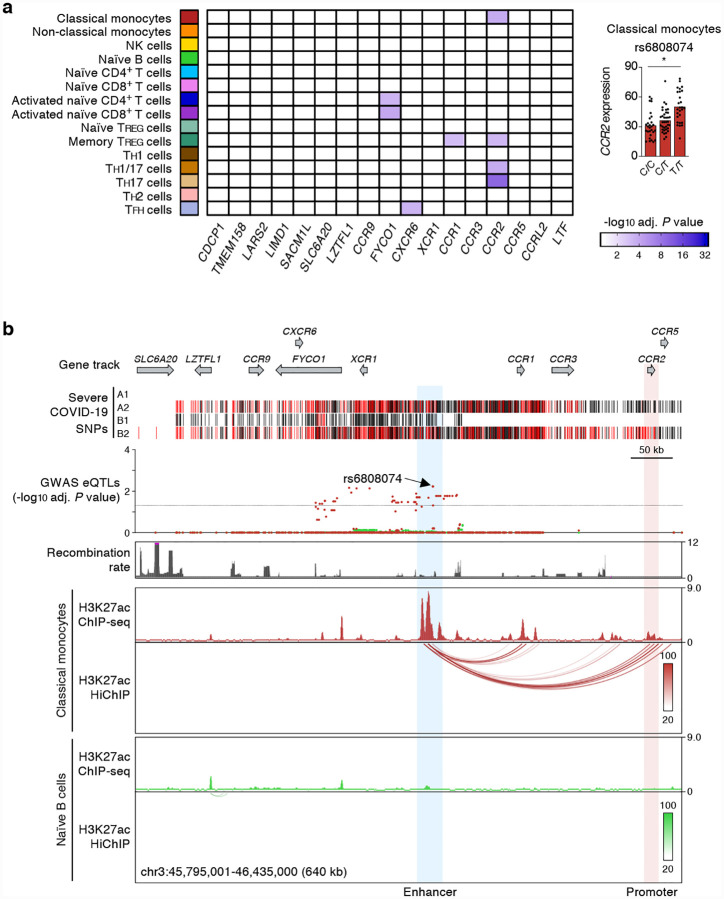
Figure 2. Promoter interacting distal cis-eQTLs regulate CCR2 promoter activity specifically in classical monocytes.
(a) Genes and cell types most susceptible to the effects of severe COVID-19-risk variants (all with GWAS association P value < 5×10−8) in the 3p21.31 locus. The adj. association P value for the peak GWAS cis-eQTL associated with the indicated eGenes in each cell type and activation condition is shown (left). Right, mean expression levels (TPM) of CCR2 gene in classical monocytes (* adj. association P value: 5.94×10−3), from subjects (n=91) categorized based on the genotype at the indicated GWAS cis-eQTL (each symbol represents an individual subject; adj. association P value calculated by Benjamini-Hochberg method). (b) WashU Epigenome browser tracks for the 3p21.31 locus, severe COVID-19-risk associated GWAS variants (based on GWAS study, see Extended Data Figure 1a; red color bars are lead GWAS SNPs, black color bars are SNPs in linkage disequilibrium), adj. association P value for GWAS cis-eQTLs associated with expression of CCR2 expression in classical monocytes (dark red) and naïve B cells (green), recombination rate tracks27,28, H3K27ac ChIP-seq tracks, and H3K27ac HiChIP interactions in classical monocytes and naïve B cells.