Figure 2.
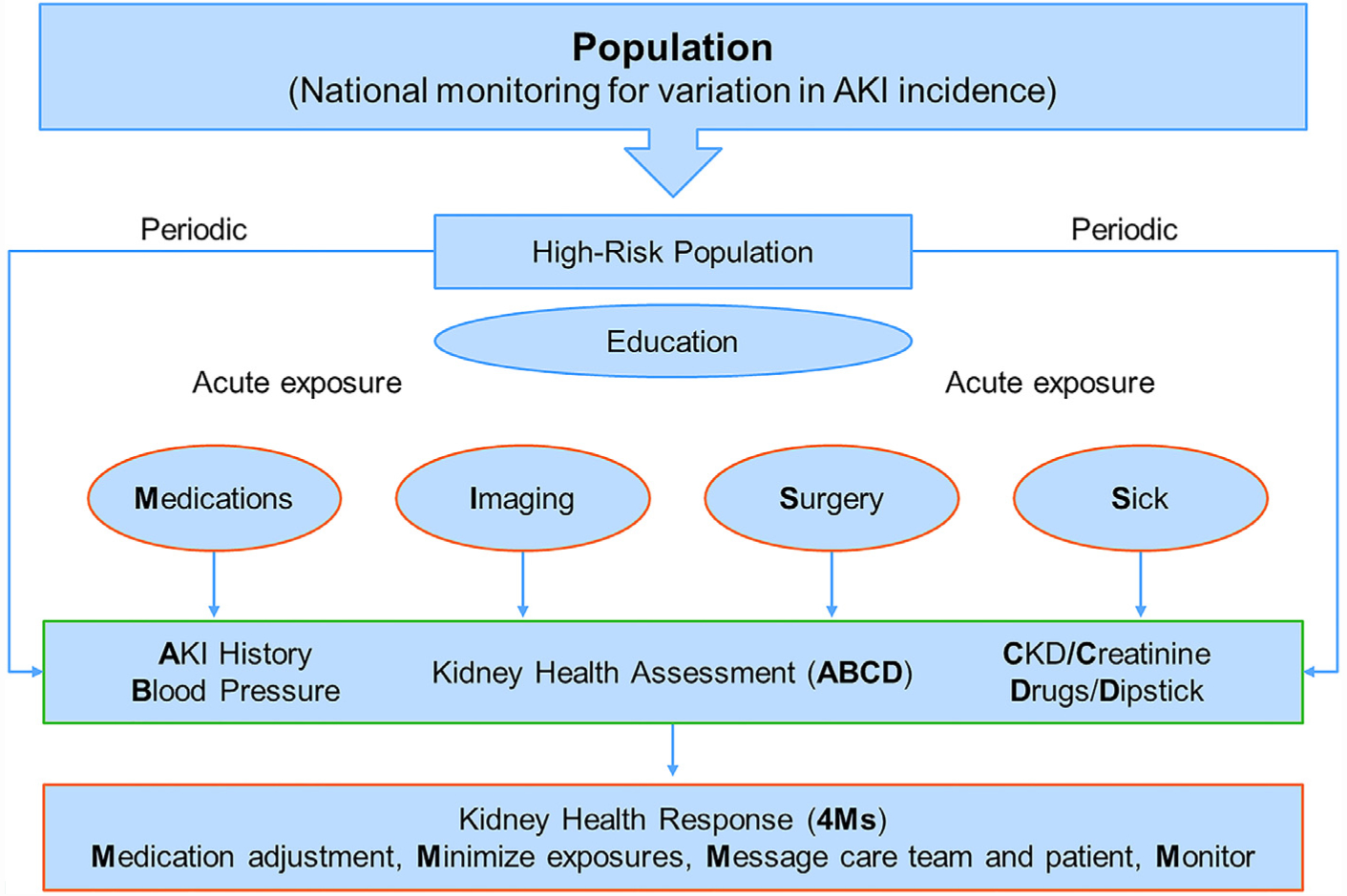
Kidney Health Assessment and Response. Strategies to identify, monitor, and prevent acute kidney injury (AKI) in the community setting, which can be modified to develop suitable quality indicators. The government and health system help with the identification and education of high-risk patients. The Kidney Health Assessment monitors these patients for AKI and chronic kidney disease (CKD) at least yearly and, more frequently, at the time of a high-risk exposure (eg, nephrotoxic medications, imaging, surgery, sickness). The Kidney Health Assessment includes AKI history, Blood pressure, serum Creatinine level, Drug list, and urine Dipstick (ABCD). This assessment should trigger a Kidney Health Response (the 4Ms) to actively prevent AKI, which encompasses cessation of unnecessary medications (eg, nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs], the minimization of nephrotoxic exposures (eg, intravenous contrast), messaging the health care team and patient to alert the high-risk of AKI, and monitoring for AKI and its consequences (eg, serum creatinine and potassium).
Source: Reprinted from Acute Disease Quality Initiative (ADQI) with permission.
