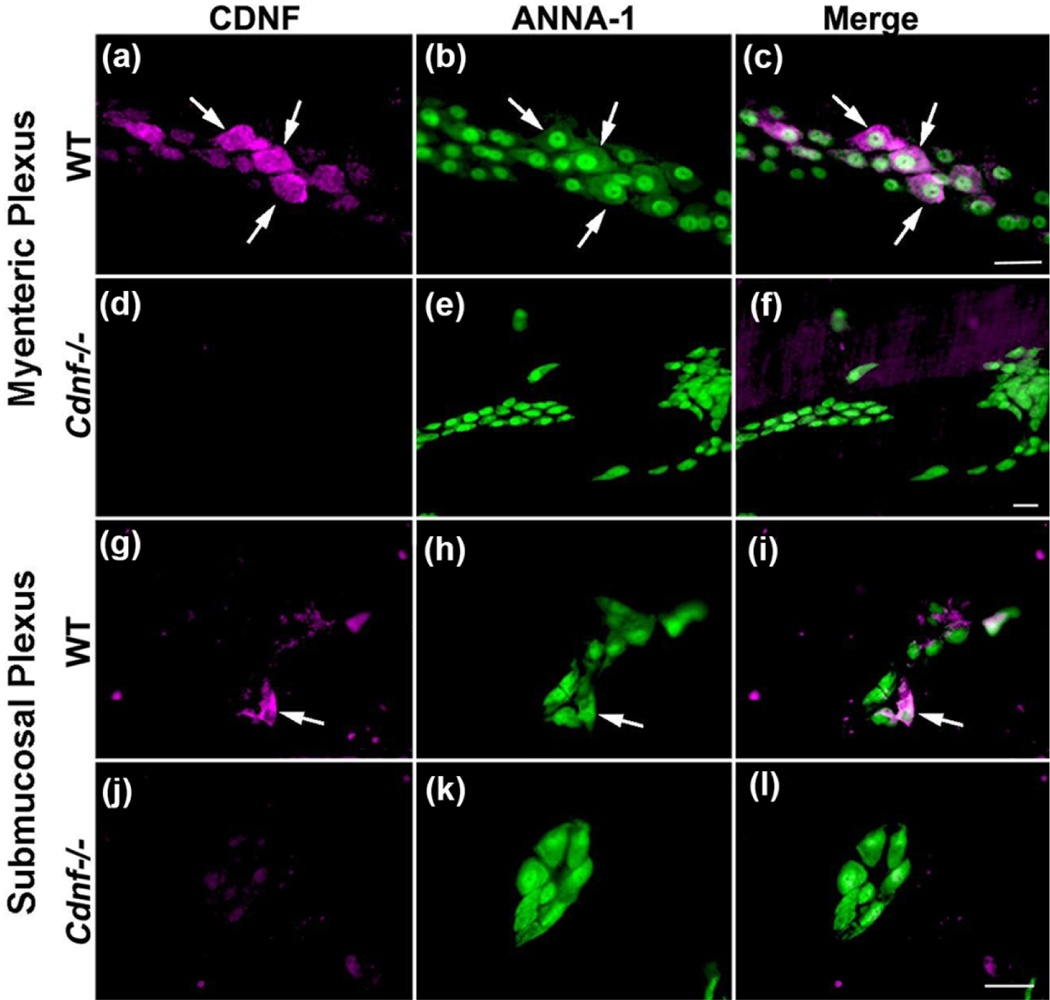
Figure 1. CDNF immunoreactivity is found in neurons of each enteric plexus.
Laminar preparations of bowel wall from the Ileum containing the myenteric (a-f) or submucosal plexuses (g-l) were dissected, immunostained to demonstrate the immunoreactivities of CDNF and the neuronal marker, ANNA-1, and viewed as whole mounts. Tissues from Cdnf+/+ (WT) and Cdnf−/− mice (11-month-old) were compared to validate the antibodies to CDNF. a-c. A ganglion of the myenteric plexus of a Cdnf +/+ mouse illuminated to reveal CDNF-immunoreactive cells (a, magenta), ANNA-1-immunoreactive cells (b, green), and the merged image (c). The arrows show the location of the same cells in each panel. The bar = 35 μm (a-c). d-f. A ganglion of the myenteric plexus of a Cdnf −/− mouse illuminated to reveal CDNF-immunoreactivity (d, magenta; no cells are immunoreactive), ANNA-1-immunoreactive cells (e, green), and the merged image (f). The bar = 35 μm (d-f). g-i. A ganglion of the submucosal plexus of a Cdnf +/+ mouse illuminated to reveal CDNF-immunoreactive cells (g, magenta), ANNA-1-immunoreactive cells (H, green), and the merged image (I). The arrow shows the location of the same cell in each panel. j-l. A ganglion of the submucosal plexus of a Cdnf −/− mouse illuminated to reveal CDNF-immunoreactive cells (j, magenta; no cells are immunoreactive), ANNA-1-immunoreactive cells (k, green), and the merged image (l). The bar = 35 μm (g-l).