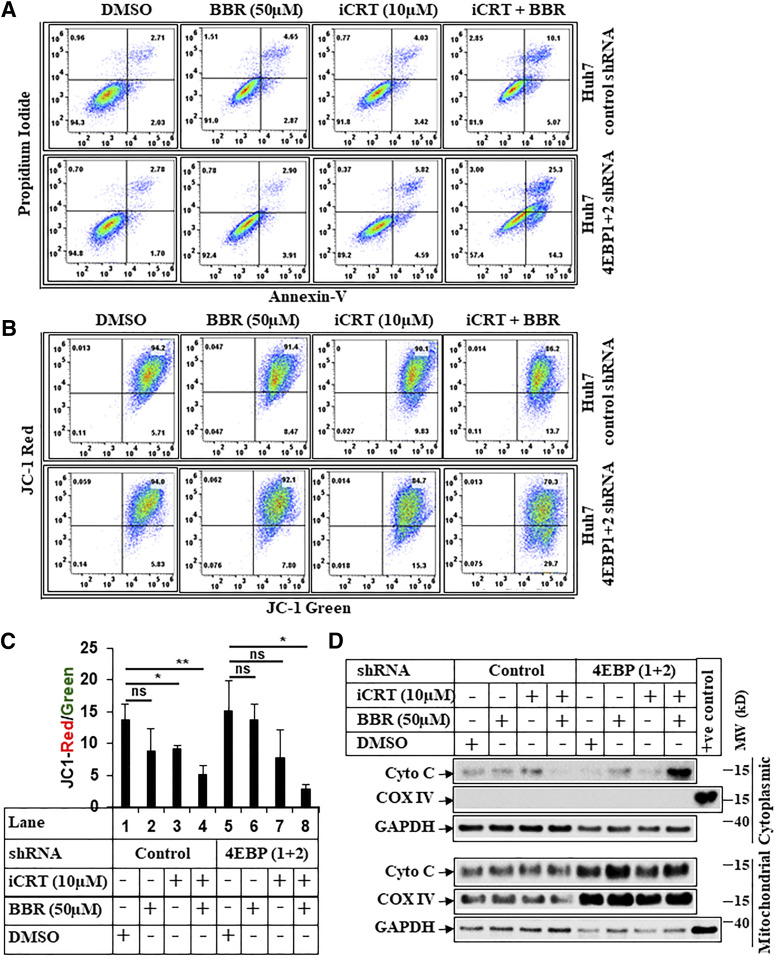
Fig. 8.
BBR induces intrinsic apoptosis via targeting β-catenin. (A) Representative picture showing flowcytometric analysis of apoptosis assays performed in Huh7-control-shRNA or Huh7-4E-BP 1+2-shRNA cells pretreated with iCRT-14 (10 µM) for 24 hours, which was followed by treatment with iCRT-14 (10 µM) alone or in combination with BBR (50 µM) for an additional 24 hours. The cells that received DMSO and BBR (50 µM) were treated with these for 24 hours. At the end of treatment, cells were harvested and subjected to apoptosis assays and analyzed similarly as described under Fig. 7A. (B) Huh7-control-shRNA or Huh7-4E-BP 1+2-shRNA cells treated as in Fig. 8A were analyzed by JC-1 assay, following procedures described under Fig. 7B. (C) The bar graphs represent the ratio of JC-1 Red/JC-1 green. The data represent ±S.D. of two independent experiments. Significant differences were determined by t test and indicated as follows: ns, P > 0.05; *P ≤ 0.05; and **P ≤ 0.01. (D) Huh7-control-shRNA or Huh7-4E-BP 1+2-shRNA cells were pretreated with iCRT-14 (10 µM) for 24 hours, which was followed by treatment with iCRT-14 (10 µM) alone or in combination with BBR (50 µM) for an additional 16 hours. The cells that received DMSO and BBR (50 µM) were treated with these for 16 hours. At the end of treatment, cells were harvested and fractionated into mitochondrial and cytoplasmic fractions and analyzed by Western blots. COX IV was used a positive control to show the purity of mitochondrial fraction, and GAPDH was used as a positive control for cytoplasmic fraction. COX IV, mitochondrial cytochrome c oxidase subunit IV; Cyto C, cytochrome c; MW, molecular weight; ns, not significant.