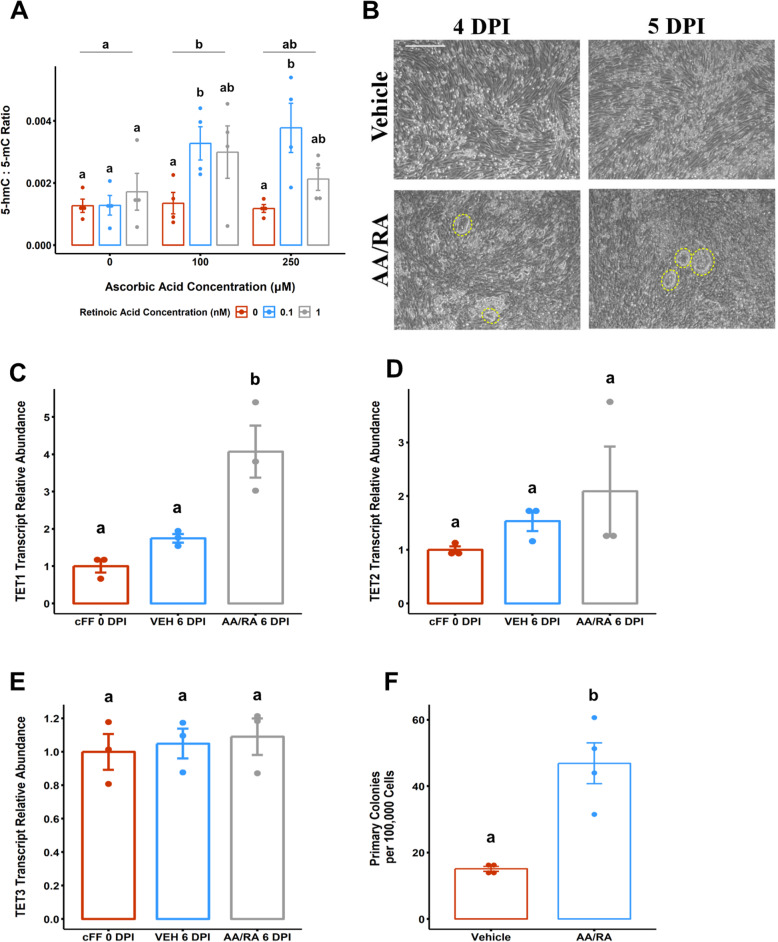
Fig. 2.
L-ascorbic acid and retinoic acid modulates 5-hmC level and promotes focal epithelialization in early canine reprogramming of TET paralogue expression. a 5-hmC to 5-mC ratio in canine fetal fibroblasts (cFFs) cultured in atmospheric oxygen and exposed to various concentrations of L-ascorbic acid (AA) and/or retinoic acid (RA). Each data point is calculated from paired aliquots from the same purified gDNA sample and analyzed by separate ELISA assay kits. b Representative phase-contrast micrographs of cFFs transduced with CytoTune-iPS 2.0 Sendai Reprogramming Kit (SeV 6:5:6) at 4 or 5 days post-infection (DPI). Transductants were treated with L-ascorbic acid and retinoic acid (AA/RA) or an equivalent volume of diluent (VEH). Yellow dashed outlines delimit areas of focal epithelial cluster formation exclusively in the AA/RA-treated transductants. Relative transcript abundance for c TET1, d TET2, and e TET3 in steady-state cFF, transduced cFF treated with VEH, or AA/RA. F Summarization of the primary colony counts (per 105 transduced cells) performed 4 days after re-seeding on mouse embryonic fibroblast feeder cells (10 DPI). Data are presented as mean ± standard error, n = 3. Means annotated with different letters are considered significantly different by two-way analysis of variance or the two-sample Mann-Whitney test, P < 0.05. Scale bars are 250 μm