Fig. 2. A cdk-12-as allele allows for the rapid depletion of CTD S2P and mimics the null mutant.
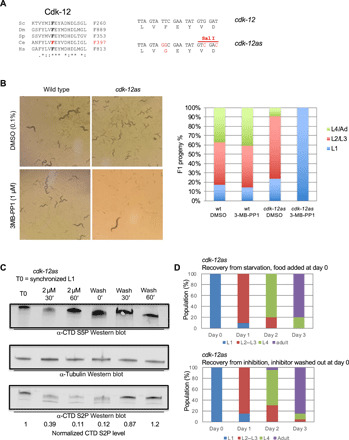
(A) Left: alignment of the residues flanking the gatekeeper phenylalanine (F) in the Cdk12 othologs from Sc (Saccharomyces cerevisae), Dm (Drosophila melanogaster), Sp (Schizosaccharomyces pombe), Ce (C. elegans), and Hs (Homo sapiens). Right: DNA sequence of the wt (TTC) and mutated (GGC) codons encoding the gatekeeper amino acid. Silent mutations introducing a Sal I restriction site used for genotyping are highlighted. (B) Left: Phenotypic analysis of wt and cdk-12-as lines cultured for 3 days in the presence or absence of 1 μM 3-MB-PP1 inhibitor. A single L4 larva was deposited at day 0. Note that the adult seen in the cdk-12-as/3-MB-PP1 condition is the parent. Right: Quantification of the phenotype of the F1 progeny grown in the indicated conditions (n = 3). (C) Western blot analysis measuring the levels of CTD S2P during inhibition of CDK-12-as and recovery. 3-MB-PP1 was added (2 μM) to synchronized L1 and later washed out at the indicated times. Total extracts were separated by polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (PAGE) and probed with anti–CTD S5P, anti–CTD S2P, and anti-tubulin for normalization. The numbers indicate the level of tubulin-normalized CTD S2P as determined by ImageJ. (D) Comparison of the recovery from starvation (top) and recovery from CDK-12-as inhibition (bottom). Hatched L1 were added to NGM plates, and the number of individuals at the indicated developmental stages was determined every day for 3 days (n = 20). Hatched L1 were added to NGM plates containing 1 μM 3-MB-PP1 inhibitor for 24 hours and transferred to NGM plates without inhibitor on day 0. The number individuals at the indicated developmental stages was determined every day for 3 days (n = 20).
