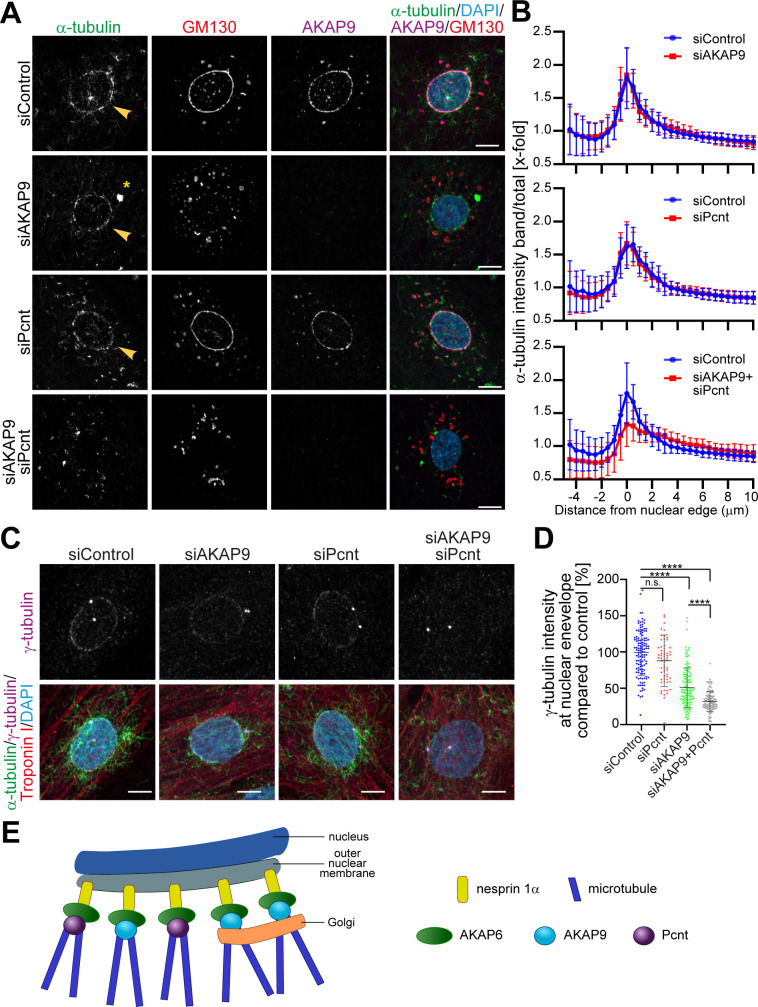
Figure 5. AKAP6 regulates two pools of microtubules at the nuclear envelope.
(A) Immunostaining of α-tubulin (green), GM130 (red), AKAP9 (magenta), and DNA (DAPI) in control, as well as in the indicated siRNA-transfected cells, after 2 min of recovery from nocodazole-induced microtubule depolymerization. Asterisks indicate centrosomal MTOC and arrowheads indicate nuclear envelope MTOC. (B) Quantification of A as α-tubulin intensity in concentric bands around the nucleus normalized to the total intensity of α-tubulin in the cell. 37 siControl cells, 53 siAKAP9 cells, 34 siPcnt cells and 43 siAKAP9+siPcnt cells were quantified per condition, from two independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (C) Immunostaining of γ-tubulin (magenta), α-tubulin (green), troponin I (red), and DNA (DAPI) in siRNA-treated cardiomyocytes after 2 min of recovery from nocodazole-induced microtubule depolymerization. (D) Quantification of C, as γ-tubulin intensity at the nuclear envelope normalized to siControl-treated cells. Statistical test: one-way ANOVA with post-hoc Bonferroni’s comparison. ****: p<0.0001, n.s.: no significance, n = 127, 63, 136, 115 (from left to right), data are pooled from three independent experiments. Error bars represent the SD. (E) Model representing the two pools of microtubules regulated by AKAP6. AKAP6 orchestrates MTOC activity at the nuclear envelope by anchoring both γ-TuRC biding proteins, Pcnt and AKAP9. While Pcnt and AKAP9 cooperate at the nuclear envelope for the nucleation of microtubules, Golgi-dependent microtubule nucleation depends on AKAP9. Scale bars: 10 µm.