Fig. 7.
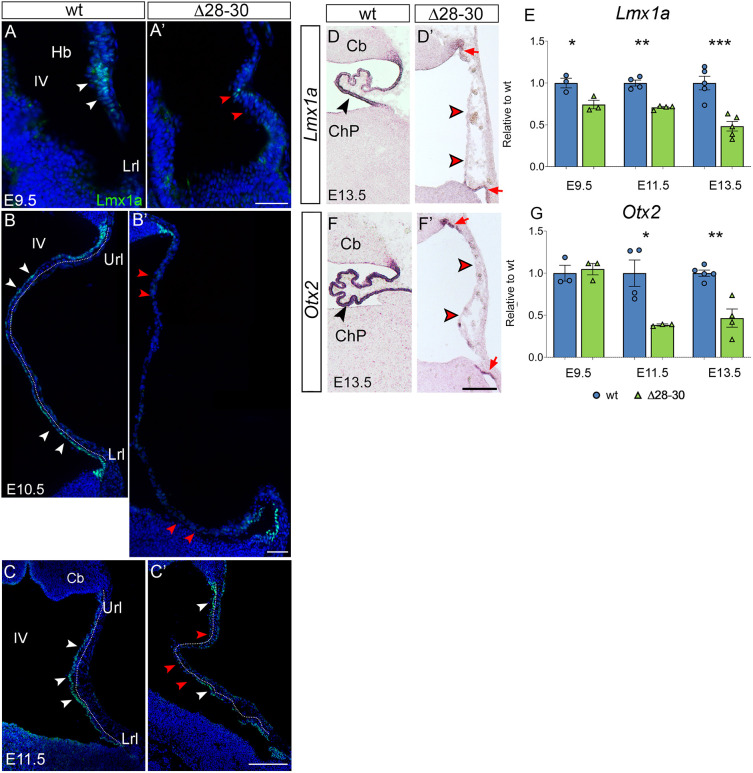
Established markers of the developing hChP are sharply downregulated in the mutant. (A-C′) Immunostaining of parasagittal cerebellar sections to visualize Lmx1a localization at different stages of development. (A-C) In the wild type at E9.5, the protein is expressed in the progenitors of the dorsal hindbrain (white arrowheads in A), while at E10.5 and E11.5 it is present in the nascent epithelium of the hChP (white arrowheads in B,C, dotted line). (A′-C′) In the mutant, Lmx1a is almost absent at all stages analyzed, and the signal, when present, is discontinuous (white and red arrowheads in A-C and A′-C′, respectively). (D,D′,F,F′) In situ hybridization of cerebellar parasagittal sections at E13.5 with Lmx1a and Otx2 riboprobes. In the wild-type hChP, Lmx1a and Otx2 are strongly expressed (black arrowheads in D,F), while in the mutant hChP, Lmx1a (D′) and Otx2 (F′) are faintly expressed in the upper and lower rhombic lip, and are absent in the hChP, which is misfolded (red arrowheads). (E,G) RT-qPCR reveals a sharp downregulation of Lmx1a and of Otx2 in the mutant hindbrain at E9.5, E11.5 and E13.5 (E9.5, n=3/genotype; E11.5, n=4/genotype; E13.5, n=5/genotype). Data are mean±s.e.m. ***P<0.0005, **P<0.005, *P<0.05 (Welch's unequal variances t-test). Hb, hindbrain; IV, fourth ventricle; Lrl, lower rhombic lip; Url, upper rhombic lip; Cb, cerebellum; ChP, choroid plexus. Scale bars: 50 μm in A-B′; 200 μm in C,C′,D,D′,F,F′.