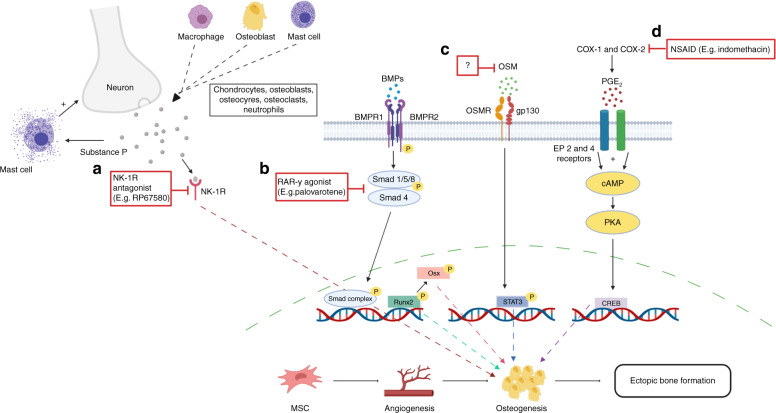
Fig. 3.
Key pathways/mechanisms implicated in the development of NHO highlighting potential and existing therapeutic targets to mitigate NHO. a Substance P receptor (NK-1R) antagonists (e.g. RP67580) have been found to reduce NHO volume in murine models. b Downstream of the BMP pathway, RAR-γ agonists such as palovarotene have been reported to prevent early stages of NHO development by disrupting OPC differentiation, chondrogenesis and osteogenesis by downregulating mRNA expression of SOX-9 and RUNX2. c OSM is a potential therapeutic target and may serve as a biomarker for NHO. Blocking OSM has been found to reduce NHO likely by inhibiting downstream transcription factor, STAT3, which is known to trigger bone formation. d NSAID, indomethacin is currently the preferred prophylaxis for NHO/HO. It targets COX-1 and COX-2 non-selectively, inhibiting the production of prostaglandins and osteogenesis (created with BioRender.com)