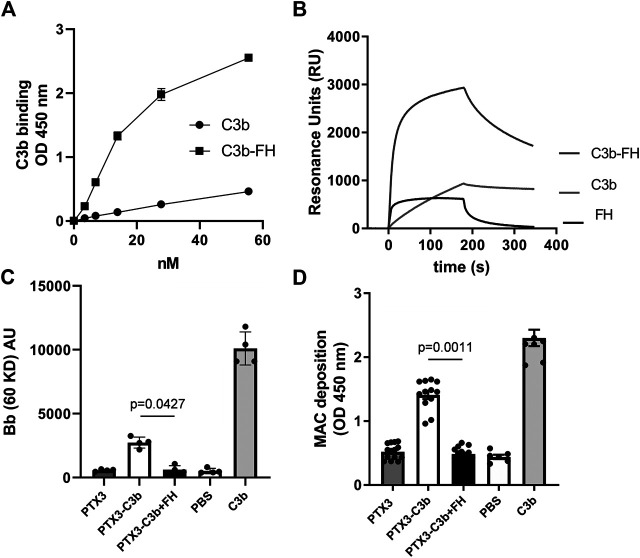
FIGURE 3.
PTX3 recruits C3b and FH on non-cellular surfaces and modulates C3bBb and MAC formation. (A) PTX3-coated wells were incubated with the indicated concentrations of C3b or mixtures of C3b and FH (at [C3b]:[FH] molar ratios of 2:1). Bound C3b was detected by ELISA, and data are presented as mean ± SEM from two independent experiments performed in triplicate (n = 6). (B) Representative SPR sensorgrams of the interaction of FH, C3b, and mixtures of C3b and FH with immobilized PTX3. (C) Microtiter plates were coated with C3b alone, PTX3 followed by C3b, or PTX3 followed by a mixture of C3b and FH, then incubated with FH-depleted human serum. Surface-bound proteins were analyzed by western blotting. Intact factor B and its proteolytic fragment Bb (indicative of C3bBb formation) were revealed as immune-reactive bands at apparent molecular weights of 93 kDa and 60 kDa. Band intensity for the Bb species was measured by densitometry. Results are expressed as mean ± SEM, n = 4. (D) Microtiter plates were coated and incubated as described in (C), and MAC deposition was assessed by ELISA using an anti-sC5b-9 antibody. Data are expressed as mean ± SEM from four independent experiments performed in duplicate (n = 8). The p-values reported in (C,D) were from the Kruskall-Wallis test, followed by Dunn’s multiple comparison test, for the PTX3/C3b and PTX3/C3b/FH complexes. Both in (C,D), C3b-coated wells were used as a positive control for C3bBb formation, and not used for statistical comparison.