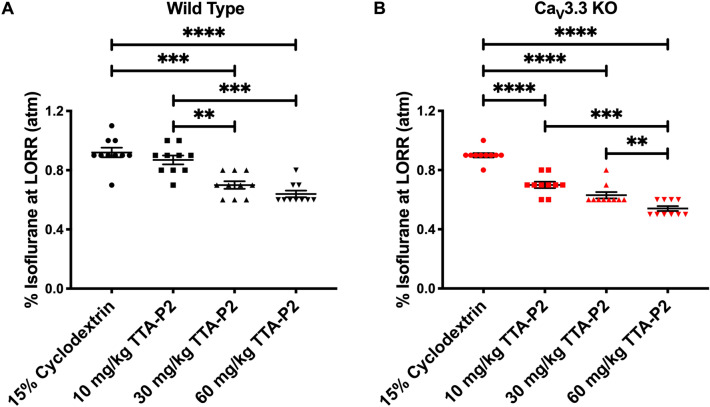
Figure 3.
Dose-dependent sparing effect of TTA-P2 on isoflurane-induced hypnosis in the mutant and WT mice. (A) Percent isoflurane at LORR for WT mice. Data from WT mice injected with vehicle in Fig. 1B is used here as baseline. WT mice have a dose dependent decrease in the % isoflurane as the dose of TTA-P2 was escalated (one-way ANOVA: F3,36 = 29.14, p < 0.001). Bonferroni multiple comparison’s test further elucidated significant differences between 15% cyclodextrin and 30 mg/kg TTA-P2 (p < 0.001), 15% cyclodextrin and 60 mg/kg TTA-P2 (p < 0.001), 10 mg/kg TTA-P2 and 30 mg/kg TTA-P2 (p = 0.007), and 10 mg/kg TTA-P2 and 60 mg/kg TTA-P2 (p = 0.001). (B) Percent isoflurane at LORR for CaV3.3 KO cohort. Data from mutant mice injected with vehicle in Fig. 1B is used here as control. Mutant mice had a dose dependent decrease in percent isoflurane for LORR as the dose of TTA-P2 increased (one-way ANOVA: F3,36 = 115.50, p < 0.001). Bonferroni multiple comparison’s test further identified significant differences between 15% cyclodextrin and 10 mg/kg TTA-P2 (p < 0.001), 15% cyclodextrin and 30 mg/kg TTA-P2 (p < 0.001), 15% cyclodextrin and 60 mg/kg TTA-P2 (p < 0.001), 10 mg/kg TTA-P2 and 60 mg/kg TTA-P2 (p < 0.001), 30 mg/kg TTA-P2 and 60 mg/kg TTA-P2 (p = 0.004).