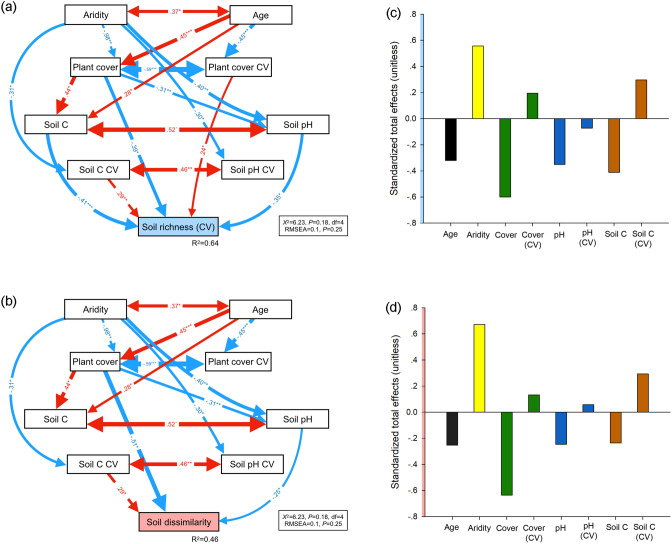
Figure 3.
Structural equation models describing the effects of aridity, age, and plant and soil attributes on the belowground spatial variability of soil richness (a) and community composition dissimilarity (b). Numbers adjacent to arrows are standardized path coefficients, analogous to relative regression weights, and indicative of the effect size of the relationship. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001. Only significant relationships (P < 0.05) are shown. Red and blue arrows indicate positive and negative relationships, respectively. Arrow widths are proportional to the strength of the relationship. The proportion of variance explained (R2) appears alongside the response variable in the model. Goodness-of-fit statistics for each model are shown in the bottom (df degrees of freedom, RMSEA root mean squared error of approximation). Panels (c,d) show the standardized total effects (direct plus indirect effects derived from the structural equation models) of the different explanatory variables on the spatial variability of belowground richness and community composition dissimilarity, respectively.