Figure 3.
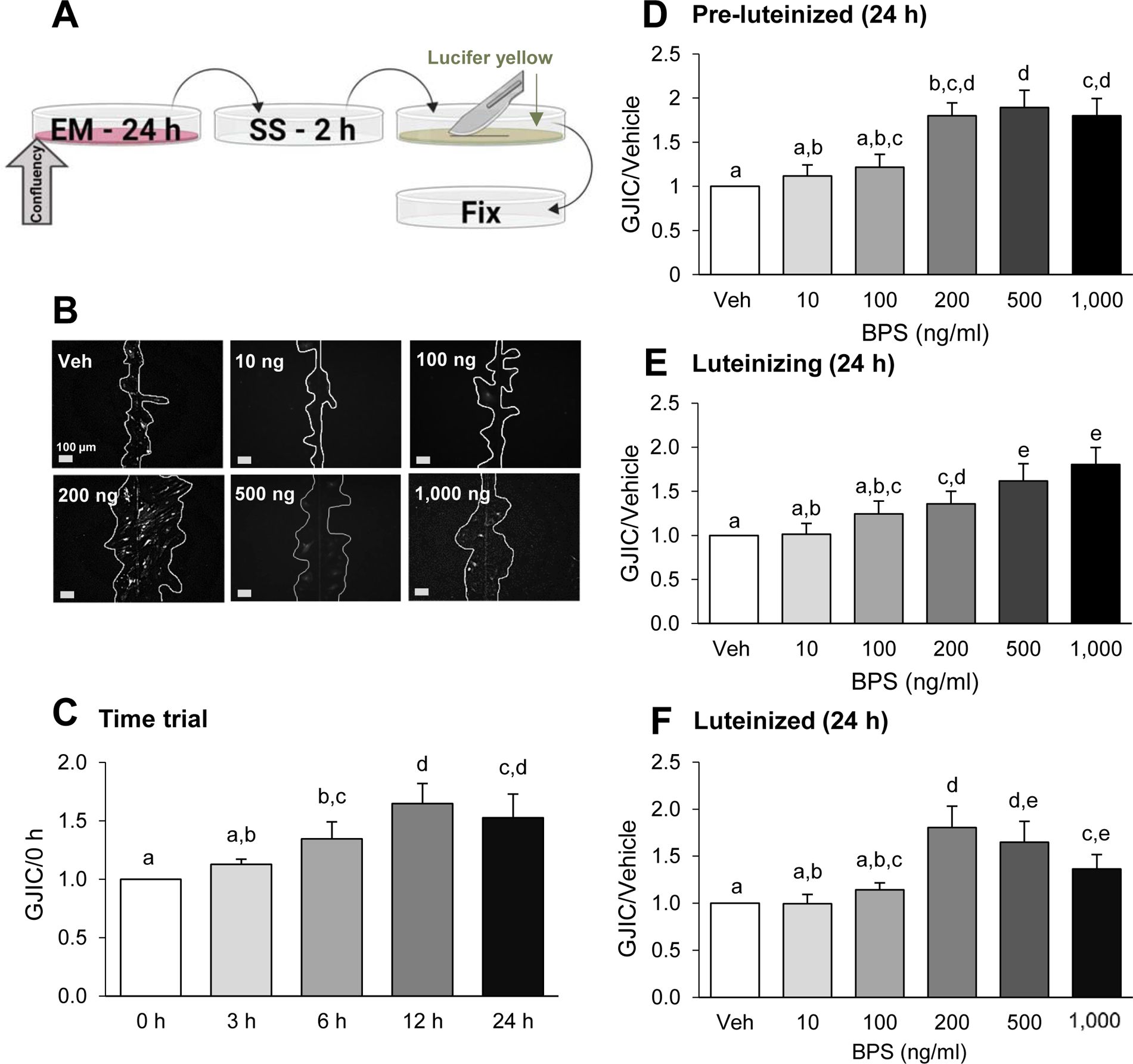
Dose- and time-dependent effects of bisphenol S (BPS) exposure on gap junction intercellular communication (GJIC) in ovine primary theca cells. Scheme of exposure (A): At ~80% confluency, cells are exposed to exposure medium (EM) containing BPS for 24 h, followed by a 2 h serum starvation (SS) period. Cells were then subjected to the scrape loading dye/transfer assay, using lucifer yellow dye (arrow) and a scalpel blade, before fixation (see text for additional details). Representative images from scrape loading dye transfer assay (B) used to assess GJIC in pre-luteinized ovine theca cells. White lines were drawn to facilitate visualization of the lucifer yellow intercellular transfer. BPS effect on GJIC (mean ± SEM) in a time-course in pre-luteinized theca cells (C) and in a dose-response in pre-luteinized (D), luteinizing (E), and luteinized (F) theca cells. The effect of BPS was normalized with the dye transfer in the vehicle control. At least 3 different theca cell cultures (each representing a biological replicate) were used for each time point, BPS dose and cellular stage. Different letters denote statistical differences among treatment groups at P < 0.05. Veh: DMSO vehicle control.
