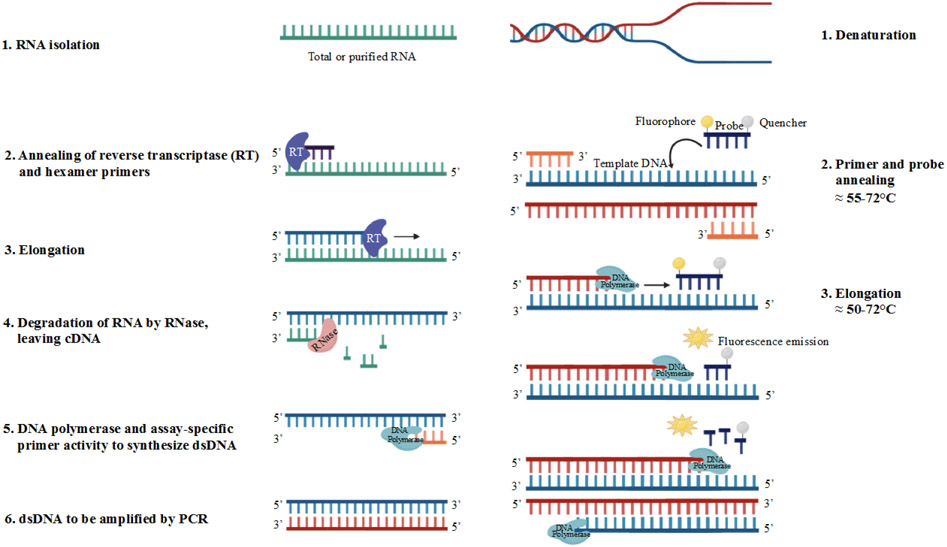
Figure 2.
Molecular underpinnings of quantitative PCR (qPCR) reactions using RNA (reverse-transcriptase qPCR; left column) or DNA (right column) as a template. [1] Purified template RNA or DNA in a reaction well (and denaturation if the template is double stranded DNA). [2] Hexamer primers and reverse transcriptase bind to target RNA or forward and reverse primers along with probe bind to template DNA. [3] Reverse transcriptase transcribes a complementary DNA strand to form a cDNA-RNA hybrid or DNA polymerase synthesizes dsDNA displacing the quencher from the probe; fluorescence emission is captured. [4] RNase hydrolyzes the RNA, leaving the cDNA strand free for [5] binding of DNA polymerase to synthesize dsDNA followed by steps [1], [2] and [3] from the qPCR reaction