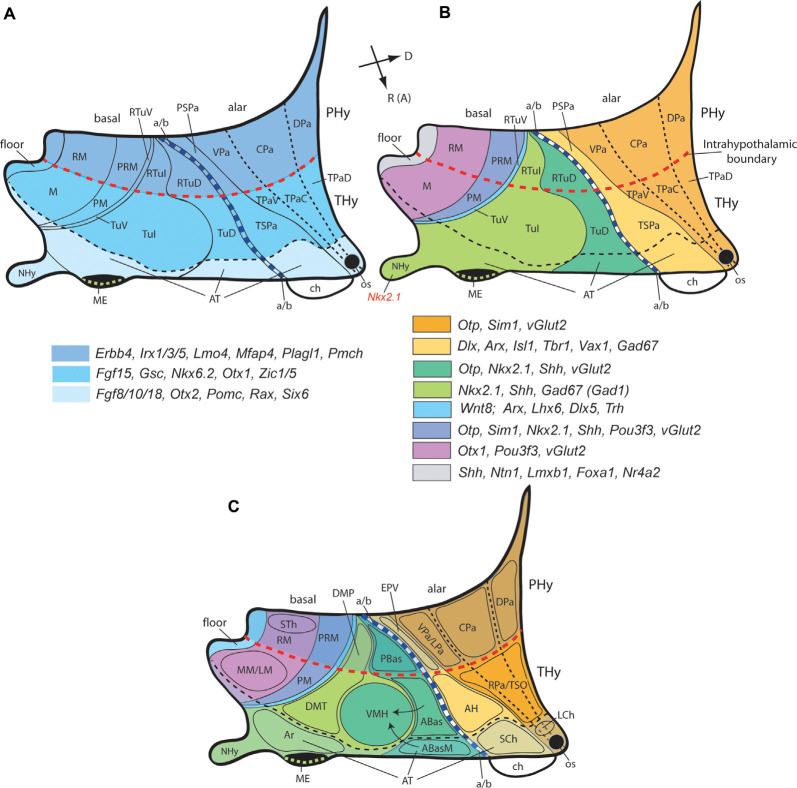
Figure 3.
Second level dorsoventral (alar and basal) histogenetic subdivisions of the hypothalamus (A), genoarchitectonic maps (B), and location of main nuclear derivatives (C) based on the updated prosomeric model (Figure 2). (A) The hypothalamus divides rostrocaudally into the terminal and peduncular parts (THy, PHy; dark blue), delimited by the intrahypothalamic boundary (transverse red dash line); the rostro median region of THy constitutes the acroterminal domain (AT; light blue), delimited by a black dash line. The longitudinal alar/basal limit (a/b; thick blue dash line) separates the alar and basal hypothalamus. The alar hypothalamus is subdivided dorsoventrally into paraventricular (Pa) and subparaventricular domains (SPa), each of them having peduncular and terminal components (e.g., PSPa, TSPa), plus the corresponding acroterminal areas. The peduncular/terminal Pa has three DV subdivisions: dorsal, central, and ventral. The basal hypothalamus is primarily subdivided dorsoventrally into tuberal/retrotuberal (Tu/RTu), perimamillary/retroperimamillary (PM/PRM), and mamillary/retromamillary areas (M/RM), plus the corresponding acroterminal parts. The large Tu/RTu area subdivides further into dorsal, intermediate, and ventral parts (TuD/RTuD, TuI/RTuI, TuV/RTuV). Rostral (or anterior; R [A]) and dorsal (D) spatial directions are indicated in (B). (B) A schematic color-coded map of characteristic genoarchitectonic patterns is differentially expressed in the hypothalamic dorsoventral subdivisions, based on Puelles et al. (2012) and Díaz et al. (2015). Labels as in (A). (C) Map of representative hypothalamic nuclei derived from the molecularly-defined progenitor PHy, THy, and AT domains illustrated in the diagrams shown in (A,B). Arrows represent ventral migrations from the dorsal anterobasal complex from the TuD area (ABas, ABasM), which generation the hypothalamic ventromedial nucleus (VMH) in the TuI area. Other abbreviations: ABas, anterobasal nucleus; ABasM, median anterobasal nucleus; AH, anterior hypothalamic area; Ar, arcuate nucleus, ch, chiasma; DMP, peduncular part of the dorsomedial nucleus; DMT, terminal part of the dorsomedial nucleus; EPV, ventral entopeduncular nucleus; LM, lateral mamillary nucleus; LCh, lateral chiasmatic nucleus; LPa, lateral paraventricular nucleus; ME, median eminence; MM, medial mamillary nucleus; NHy, neurohypophysis; os, optic stalk; PBas, posterobasal nucleus; RPa, rostral paraventricular nucleus; SCh, suprachiasmatic nucleus; STh, subthalamic nucleus; TSO, terminal supraoptic nucleus.