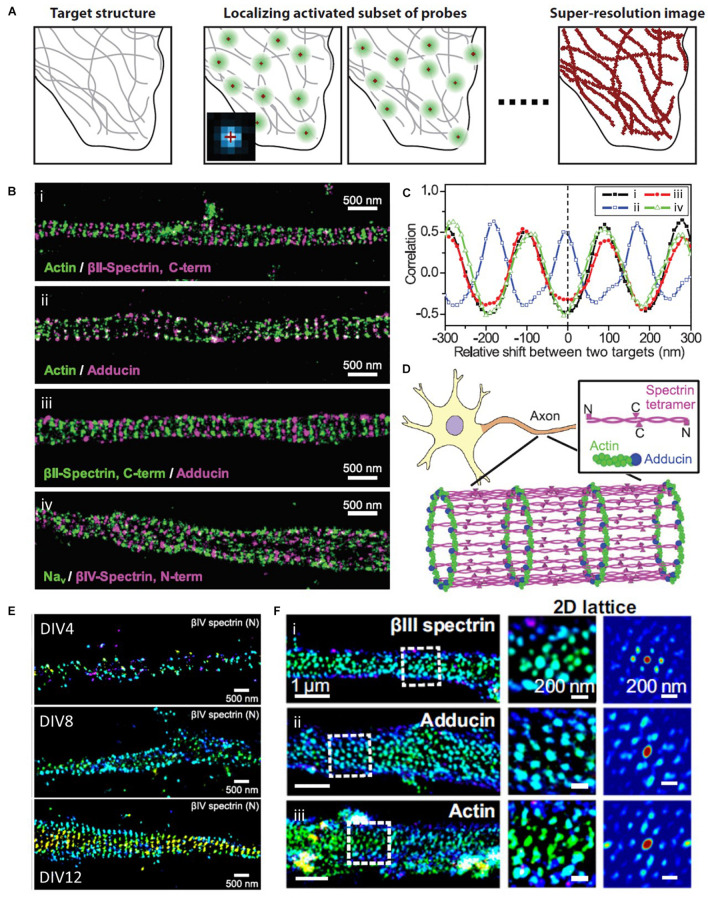
FIGURE 7.
Super-resolution STORM images of actin and ABPs. (A) The principle of SMLM, such as STORM, PALM, and FPALM. Reprinted by permission from Annual Reviews (Huang et al., 2009). (B) Two-color STORM image of (i) actin (green) and βII-spectrin C terminus (magenta), (ii) actin (green) and adducin (magenta), (iii) βII-spectrin (green) and adducin (magenta), and (iv) sodium channels (Nav, green) and βIV-spectrin N terminus (magenta). (C) Spatial correlations between actin and the βII-spectrin C terminus [(i), black], between actin and adducin [(ii), blue], between adducin and the βII-spectrin C terminus [(iii), red], and between sodium channels and the βIV-spectrin N terminus [(iv), green], which are calculated for varying relative shifts between the two color channels along the axons. (D) A model for the cortical cytoskeleton in axons, forming ring-like structures wrapping around the circumference of the axon with a periodicity of ∼180 to 190 nm. Reprinted by permission from the American Association for the Advancement of Science (B∼D) (Xu et al., 2013). (E) Representative STORM images at different developmental stages, showing assembly of AIS components into the periodic lattice structure during late developmental stages. Reprinted by permission from Zhong et al. (2014). (F) MPS components form 2D polygonal lattice structures in some somatodendritic regions of neurons. (Left) 3D STORM image of a dendritic region from a DIV 28 mouse neuron stained for (i) βIII-spectrin, (ii) adducin, and (iii) βIII-spectrin. (Middle) Zoom-in image of the region indicated by the white dashed box in the Left. (Right) 2D autocorrelation function of this boxed region, which shows a 2D periodic lattice pattern. Reprinted by permission from PNAS (E,F) (Han et al., 2017).