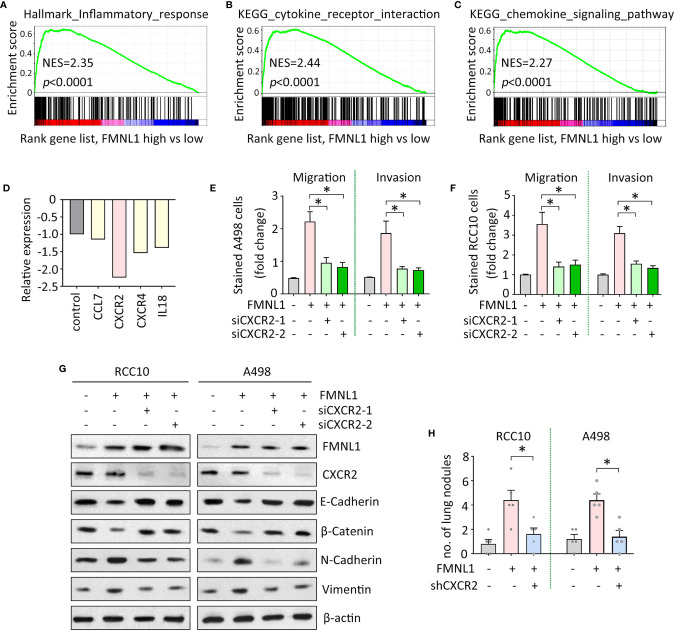
Figure 4.
FMNL1 exerts pro-metastatic activity via CXCR2 in ccRCC. (A–C) Gene sets enrichment analysis (GSEA) based on TCGA data showed that pathways involved in inflammation were activated in ccRCC patients with high expression of FMNL1. (D) PCR microarrays containing 84 genes were used to disclose the mechanism of FMNL1-induced cell migration. Genes related to inflammation were chosen for further validation. (E, F) Cells with FMNL1 overexpression were transfected with CXCR2 siRNAs. Cell migration and invasion were determined by transwell assays in A498 (E) and RCC10 (F) cells *P < 0.05. (G) Proteins were extracted from cells treated as described in E were subjected into western blot to determine the expression of EMT markers, such as E-Cadherin, β-catenin, N-Cadherin and Vimentin. β-actin served as loading control. (H) CXCR2 shRNA was introduced into RCC10 and A498 stable cells with FMNL1 overexpression. Stable cells were injected into nude mice for 40 days. Metastatic nodules in the lungs were counted and indicated by histogram. *P < 0.05.