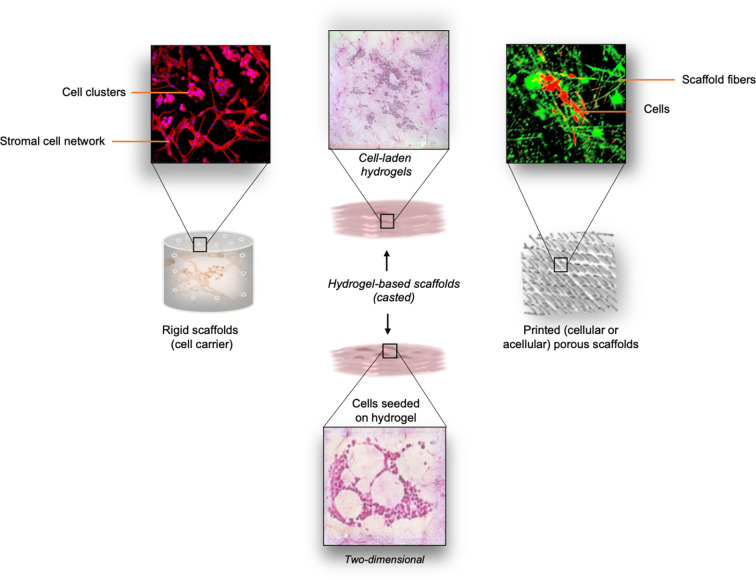
Figure 2.
Overview of different types of scaffolds explored for neuroblastoma studies. Left panel: Thermal sintering-based approach used for the fabrication of cell-free (rigid) scaffolds with defined geometry. These scaffolds provide mechanical support for cell growth. Cell morphology and cell distribution inside the interconnecting microchannels is directly influenced by the structure of the scaffold. Middle panel: Cast cell-laden hydrogels are used as the biomimetic ECM support for the embedded cells. As an option, cells can be seeded on top of the pre-made hydrogel structure. Right panel: Printing (e.g. microextrusion, drop-on-demand, laser-based printing) of various bioinks can be adopted for the scaffolding process. Both cellular and acellular approaches can be adopted for the generation of porous scaffolds with defined spatial distribution of the bioink.