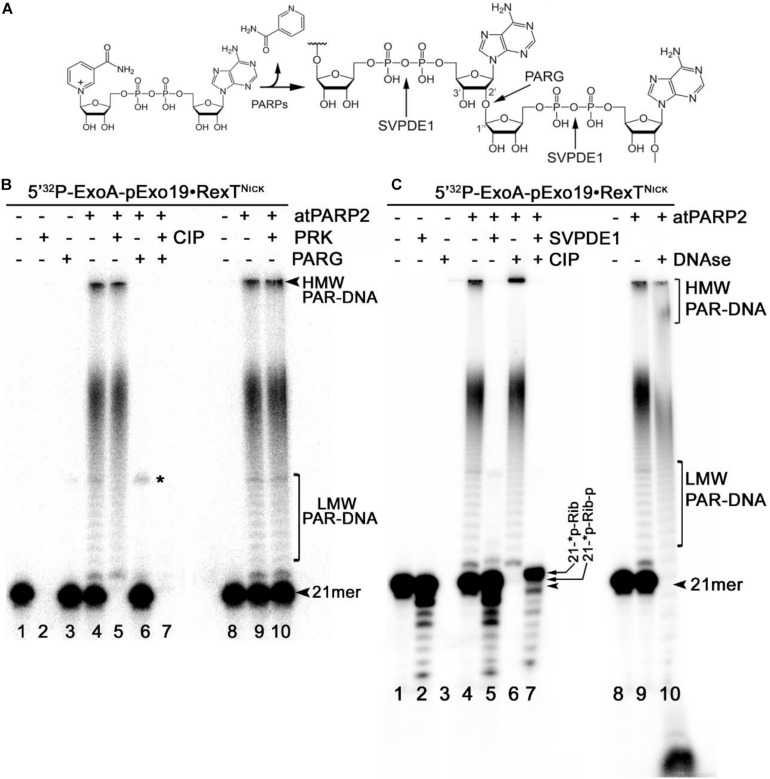
FIGURE 6.
Analysis of the products of enzymatic digestion of the PAR–DNA adducts. PAR–DNA products were generated by incubation of 20 nM 5′-[32P]-ExoA pExo19•RexTNick oligonucleotide duplex (S13) with 250 nM atPARP2 in the presence of 1 mM NAD+ for 30 min at 37°C. After reactions, the samples were heated for 20 min at 80°C and then incubated in the presence of either 50 pg•μl–1 PARG (in ADPR buffer), or 50 μg•ml–1 proteinase K, or 0.1 U SVPDE1 (in SVPDE1 buffer) or 10 U CIP (in CIP buffer) for 60 or 30 min at 37°C, respectively. (A) Graphical representation of the formation of poly(ADP-ribose) polymer and enzyme cleavage sites. (B) Denaturing PAGE analysis of the products of PARG- and proteinase-catalyzed digestion of the 5′-[32P]-labeled PAR–DNA products. (C) Denaturing PAGE analysis of the products of SVPDE-, CIP-, and DNase-catalyzed digestion of the 5′-[32P]-labeled PAR–DNA products. Arrows indicate HMW and LMW PAR–DNA products and the 21-mer free oligonucleotide. Asterisk indicates a non-specific ligation product produced by E. coli NAD+-dependent DNA ligase A.