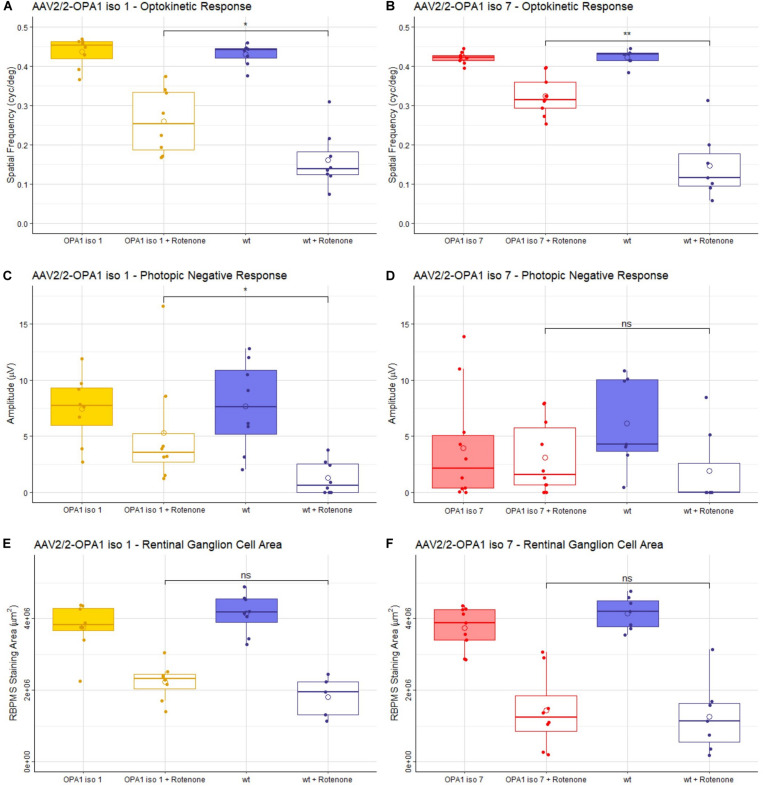
FIGURE 4.
Analysis of AAV2/2-OPA1 iso 1 and AAV2/2-OPA1 iso 7 treatment in a rotenone induced model of optic neuropathy. Adult 129 S2/SvHsd mice were intravitreally injected in both eyes with 1 × 109 vg of either AAV-OPA1 iso 1 or AAV-OPA1 iso 7 and 1 × 108 vg of AAV-CBA-EGFP, 3 weeks post AAV delivery 0.6 μl 1.5 mM rotenone was administered intravitreally. (A,B) optokinetic response, maximum spatial frequency (cyc/deg), measured 3 weeks post-rotenone administration. Rotenone treated wt animals in both cohorts show a significant decrease in OKR which is significantly improved by AAV2/2-OPA1 iso 1 or 7 treatment (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01, respectively). (C,D) Show the photopic negative response (PhNR) measured 2 weeks post-rotenone. AAV2/2-OPA1 iso 1 treated animals administered with rotenone show significant protection of PhNR amplitudes compared to wt animals given rotenone (p < 0.05), however, AAV2/2-OPA1 iso 7 treated eyes administered with rotenone only showed a modest trend toward protection (p≈ 0.2). (E,F) Show the area of RBPMS staining (μm2) as a measure of RGC cell survival. Neither treatment showed statistically significant benefit in RGC area, however, AAV2/2-OPA1 iso 1 should a modest trend toward protection (p ≈ 0.2). Open circle = mean, OPA1 iso 1 and 7 ± rotenone; n = 7; wt ± rotenone, n = 8 (OPA1 iso 1 cohort) and wt ± rotenone, n = 10 (OPA1 iso 7 cohort) pairwise Wilcoxon rank sum test with BH correction (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01).