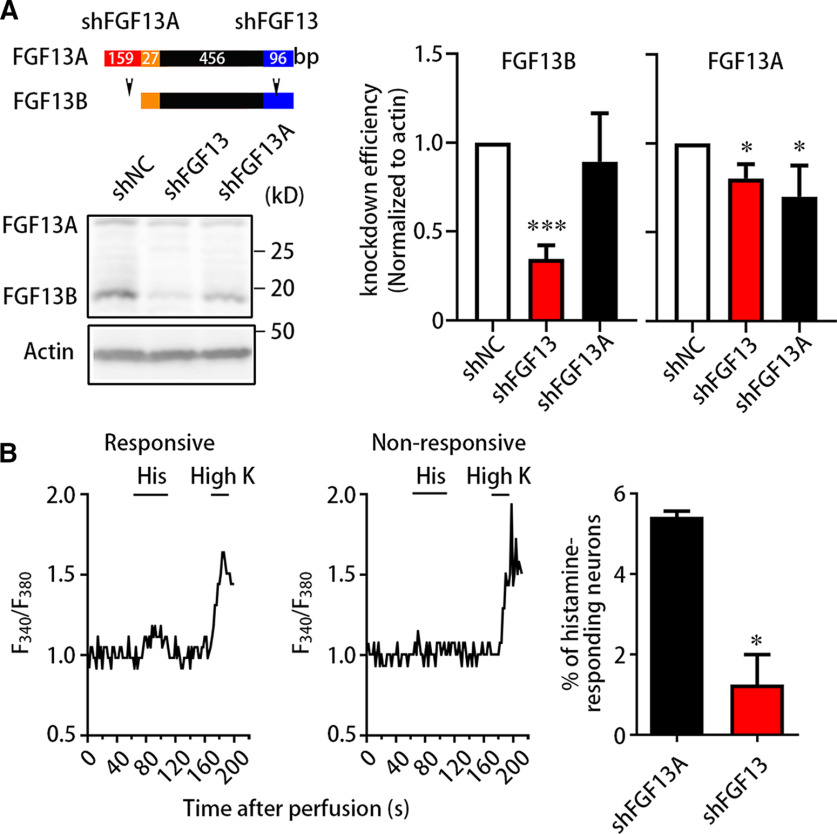
Figure 2.
FGF13B mediates the histamine-induced neuronal response. A, Immunoblotting showing shRNA-mediated knockdown of FGF13 isoform. Schematic diagram of shRNAs designed to target against FGF13A mRNA (shFGF13A) and FGF13A/B mRNA (shFGF13) (top left). Immunoblotting displayed that the FGF13B expression was significantly reduced in neurons treated with shFGF13, instead of shFGF13A and shNC. Data were quantified and plotted as normalized values versus FGF13B from neurons treated with shNC (right). The FGF13B level was largely dropped in neurons treated with shFGF13 but almost unaltered in neurons treated with shFGF13A, and the FGF13A level was reduced in neurons treated with both shFGF13 and shFGF13A. Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05; ***p < 0.001; versus shNC. B, Calcium imaging showing reduced percentage of histamine-responding neurons after knockdown of FGF13. Representative traces of calcium imaging were exhibited from histamine-responding neurons and histamine-nonresponding neurons (left) treated with shFGF13 or shFGF13A. The percentage of histamine-responding neurons was markedly reduced in neurons treated with shFGF13 (n = 4 from 1 or 2 mice each, 185 cells), compared with neurons treated with shFGF13A (n = 4 from 1 or 2 mice each, 277 cells) (right). Data are mean ± SEM. *p < 0.05 versus shFGF13A.