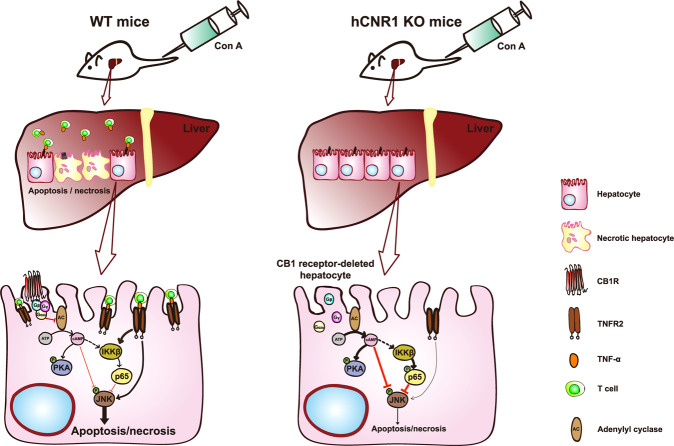
Fig. 7. Schema of the suggested protective mechanism of hepatic cannabinoid 1 (CB1) receptor nullification/blockade on liver injury by Con A treatment.
Nullification of hepatocyte-specific CB1 receptor reduces infiltration of T cells containing membrane-bound TNF-α in liver and reduces TNFR2 levels in isolated hepatocytes. Interaction between membrane-bound TNF-α and TNFR2 results in the activation of JNK and apoptotic cell death in WT mice. hCNR1−/− mice also have increased cAMP levels and PKA activation, and consequently decreased phosphorylation of JNK. Additionally, CB1 receptor-deleted hepatocytes have higher expression of phosphorylated NF-κB subunit, p65 (S536), via activation of IKKβ resulting in the protection of hepatocytes against apoptotic cell death.