Figure 6:
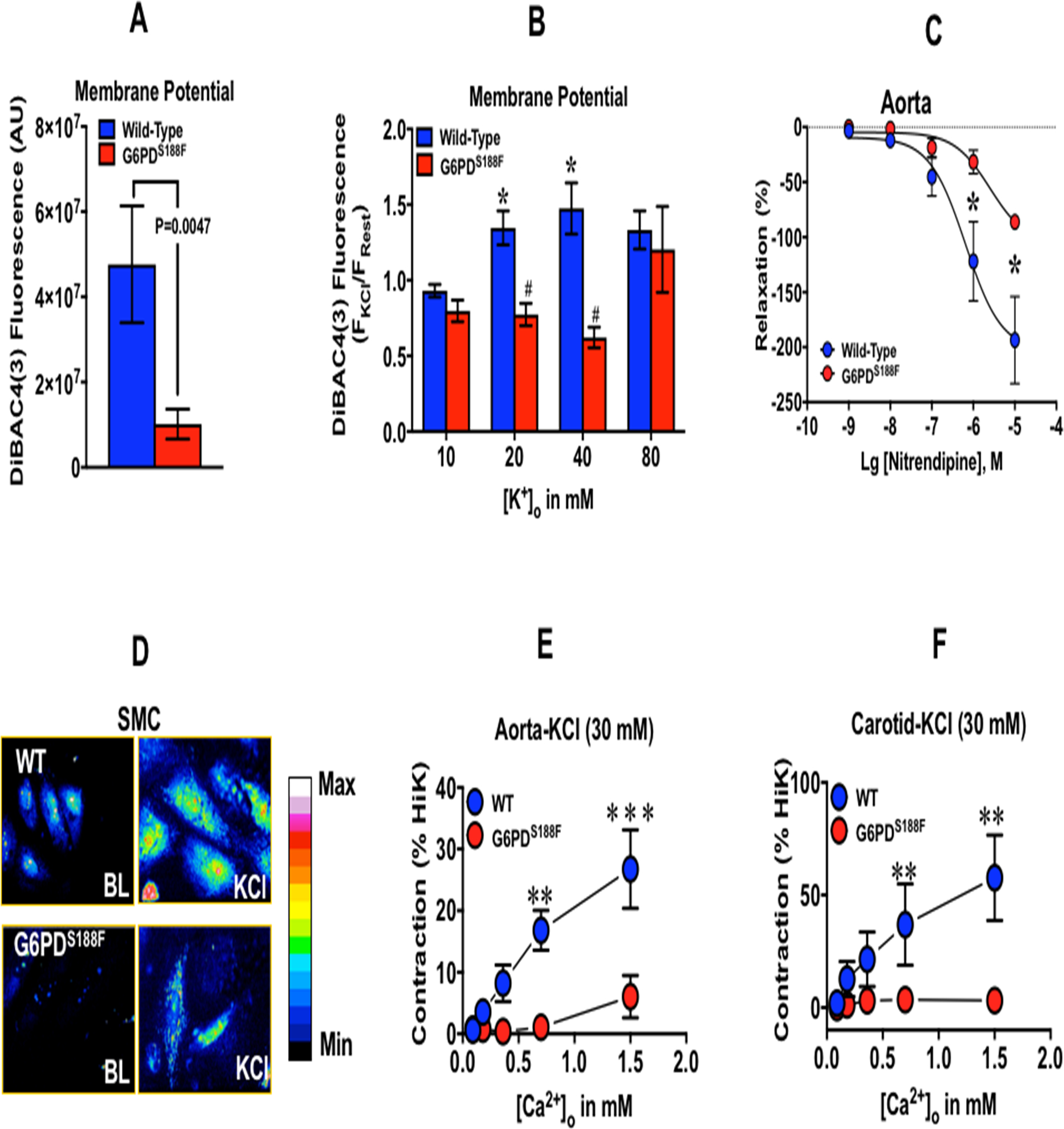
Membrane potential, nitrendipine-mediated relaxation, intracellular Ca2+, and Ca2+-mediated contraction of arteries isolated from WT and G6PDS188F rats. Membrane potential of (A) resting and (B) KCl-treated aorta was determined by the fluorescence (f480/520) of DiBAC4(3). N= 5 WT and G6PDS188F rats. (C) The effect of nitrendipine, a L-type Ca2+ channel blocker that inhibits channel activity at higher membrane potential, on aorta pre-contracted with KCl (30 mM). N= 5 WT and G6PDS188F rats. (D) A representative confocal image of four experiments demonstrating intracellular Ca2+ determined by Fluro-4 (f480/520) in aortic SMCs. Extracellular Ca2+-elicited contraction of aorta (E) and carotid artery (F) pre-contracted with KCl (30 mM) is shown. Aorta (N= 5 WT and 10 G6PDS188F rats) and carotid artery (N= 5 WT and 9 G6PDS188F rats).
