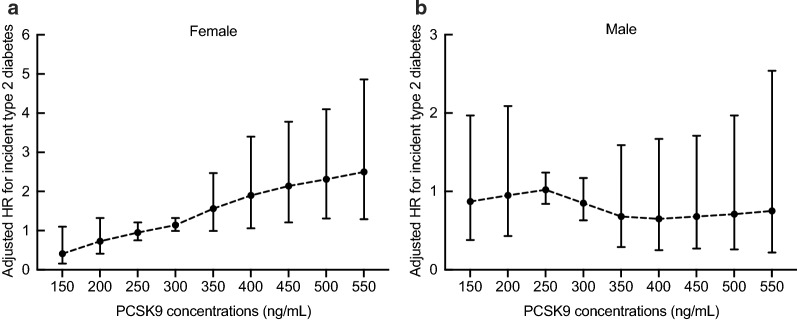
Fig. 4.
HRs (95% CI) for the 3.1-year risk of incident type 2 diabetes at different levels of PCSK9 (150–550 ng/mL) were analyzed by multivariable Cox regression models with restricted cubic splines after adjusting for age, smoking, drinking, physical activity, educational attainment, BMI, waist circumference, TG, LDL-C, SBP, ALT, AST, GGT, CRP, and HOMA-IR. Although there is overlap of confidence intervals in adjusted HRs at different PCSK9 concentrations, it appears that the trend is generally increasing with significant link for females. The reference standard was a sex-specific median PCSK9 level of 272.36 ng/mL for females and 267.56 ng/mL for males; p values < 0.001 for the overall association in females and > 0.05 in males