Figure 3. Effect of endothelial‐specific regulator of G‐protein signaling 5 deletion (EC‐Rgs5 –/–) on cerebral injury following transient middle cerebral artery occlusion (MCAO).
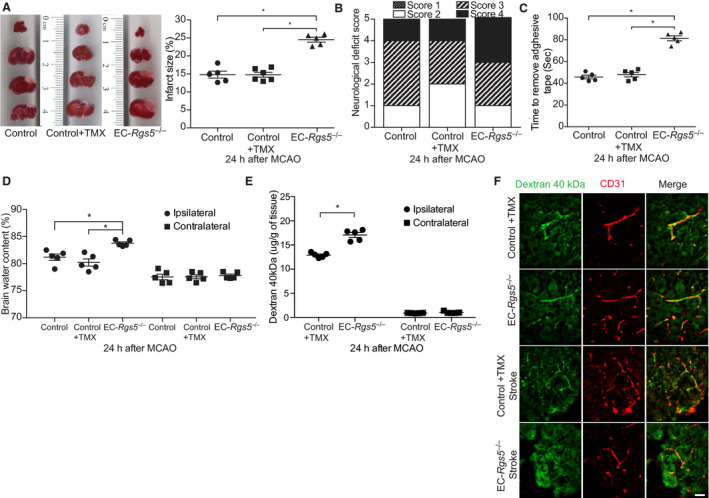
A, Coronal sections stained with 2,3,5, triphenyltetrazolium chloride (left panel) with quantification of cerebral infarct volume (right panel) (n=5 to 6). Evaluation of neurological deficit score (B) and sensorimotor impairment (C) in inducible Cre recombinase under the control of the vascular endothelial cadherin promoter mice (Cdh5‐CreERT2) tamoxifen treated (Control+TMX), and EC‐Rgs5 –/– with and without (Control) tamoxifen induction (n=5). D, Brain water content following MCAO in EC‐Rgs5 –/– and control mice (n=5). Quantification of blood‐brain barrier permeability (E) and microscopic visualization of fluorescein isothiocyanate–labeled dextran 40 kDa leakage (F), 24 hours after MCAO in EC‐Rgs5 –/– and Cdh5‐CreERT2 tamoxifen treated (Control+TMX) (n=5). Bar=50 μm. For all data sets, 1‐way ANOVA (A and C) or 2‐way ANOVA (D and E; variables, ipsilateral vs contralateral and type of mouse) was conducted followed by post hoc Tukey tests. The χ2 test was used for neurological deficit score data. *P<0.01.
