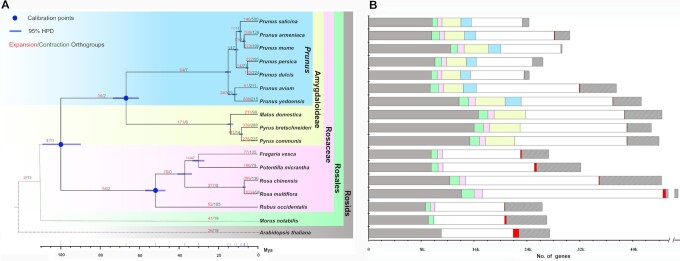
Figure 2:
Evolution of P. salicina genome and orthogroups. (A) Phylogeny, divergence time, and orthogroup expansions/contractions for 17 rosids species. The tree was constructed by maximum likelihood method using 341 single-copy orthogroups. All nodes have 100% bootstrap support. Divergence time was estimated on a basis of 3 calibration points (blue circles). Blue bar indicates 95% highest posterior density (HPD) for each node. The numbers in red and green indicate the numbers of orthogroups that have expanded and contracted along particular branches, respectively. (B) Comparison of genes among 17 rosids. The grey bars indicate the genes belonging to 9,616 rosids-shared orthogroups in each of 17 rosids. The grey + green bars indicate the genes belonging to 10,447 rosales-shared orthogroups in each of 16 rosales. The grey + green + pink bars indicate the genes belonging to 11,098 Rosaceae-shared orthogroups in each of 15 Rosaceae. The grey + green + pink + yellow bars indicate the genes belonging to 13,963 rosaceae-shared orthogroups in each of ten Amygdaloideae. The grey + green + pink + yellow + blue bars indicate the genes belonging to 15,512 Prunus-shared orthogroups in each of 7 Prunus species. The red and striped bars indicate the genes in species-specific orthogroups and unassigned genes, respectively. The white bars indicate the remaining genes for each genome.