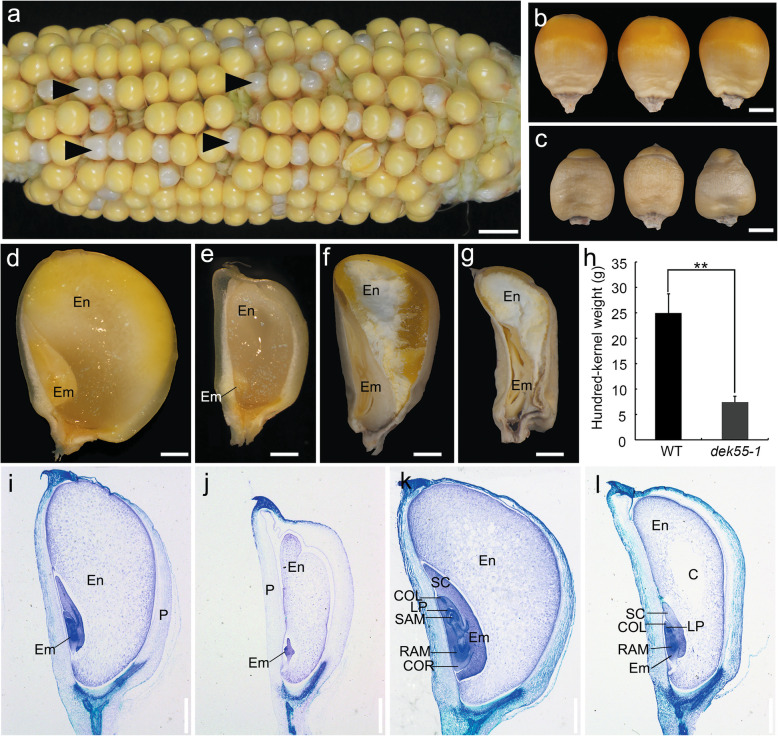
Fig. 1.
Phenotypic characterization of dek55–1 kernels. a Self-pollinated dek55–1 heterozygous ears at 15 DAP. Several mutant kernels are indicated with arrowheads. Scale bars = 1 cm. b-c Mature kernels of WT and dek55–1 plants. b. WT. c, dek55–1. Scale bars = 2 mm. d-g Comparative anatomy of WT and dek55–1 kernels at 15 DAP and at maturity. d and f WT kernels. e and g dek55–1 kernels. Scale bars = 1 mm. h Hundred-kernel weight of WT and dek55–1 kernels at maturity. (The asterisks indicate significant differences; **, P < 0.05, Student’s t-test.). i-l Histological analysis of WT and dek55–1 kernels at 12 and 18 DAP. i and k WT at 12 and 18 DAP, respectively. j and l dek55–1 kernels at 12 and 18 DAP, respectively. Scale bars = 1 mm. En, endosperm; Em, embryo; P, pericarp; LP, leaf primordium; RAM, root apical meristem; SAM, shoot apical meristem; SC, scutellum; COL, coleoptile; COR, coleorhiza; C, cavity