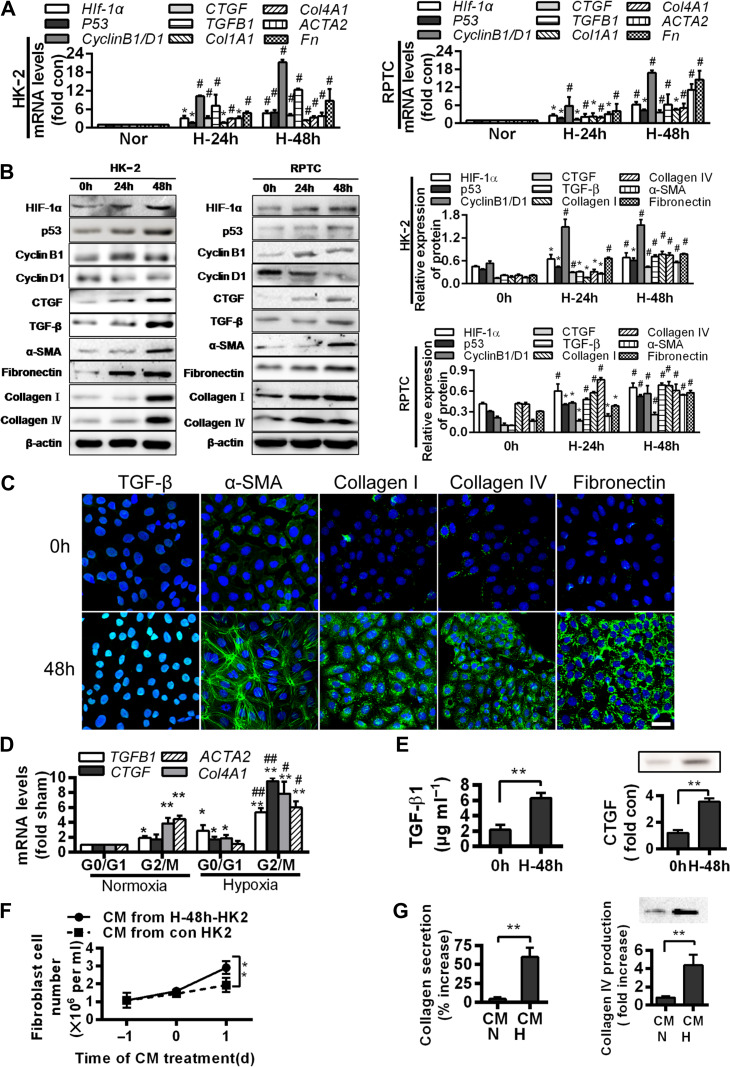
Figure 2.
G2/M arrest during hypoxia induces the production of profibrogenic factors and extracellular matrix proteins. (A) Quantitative RT-PCR analyses for mRNA levels of the indicated genes in normoxic or hypoxic (24 and 48 h) HK-2 (left) and RPTC (right) cells. *P < 0.05, #P < 0.001 vs. normoxic cells. (B) Western blotting analyses for protein levels of the indicated proteins in normoxic or hypoxic (24 and 48 h) HK-2 and RPTC cells. Representative blots are shown (left) and histograms show the relative protein levels normalized to the loading control β-actin (right). (C) Immunofluorescence analyses of TGF-β, α-SMA, collagen I, collagen IV, and fibronectin expressions (green) and DIPA (blue) in HK-2 before and after 48 h hypoxia. Scale bar, 10 μm. (D) mRNA levels of profibrogenic factors in normoxic and hypoxic HK-2 cells in various cell cycle phases. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01 vs. normoxia in G0/G1; #P < 0.05, ##P < 0.01 vs. normoxia in G2/M. (E) TGF-β1 production (left) and CTGF protein level (right) increase in the supernatant of HK-2 under hypoxia for 48 h. **P < 0.01 vs. 0 h. (F and G) Effects of conditioned media (CM) from normoxic or hypoxic HK-2 on the proliferation of NIH3T3 fibroblasts (F) and productions of collagen I (G, left) and collagen IV (G, right) in fibroblasts. **P < 0.01. Data are presented as mean ± SEM from at least three experiments.