Figure 3.
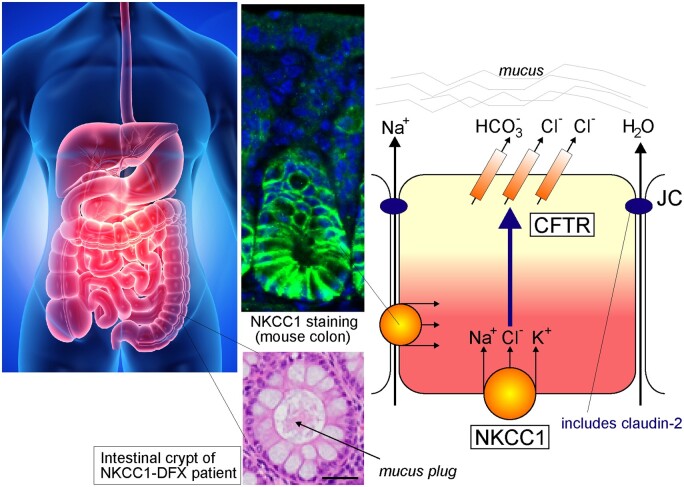
Role of NKCC1 in Fluid Secretion in the Intestine. Throughout the gastrointestinal tract, NKCC1 is expressed on the basolateral membrane of Cl− secreting epithelial cells. As seen by immunofluorescence, string NKCC1 signal (green) is observed at lateral membranes of mouse colonic epithelial cells, while some weaker signal is seen at the base. The hematoxylin/eosin panel located above shows a stained crypt lumen plugged with mucus in the colon of the NKCC1-DFX patient. The model depicts the pathway for Cl− movement through a basolateral NKCC1 and apical CFTR Cl− channel. CFTR is also permeant to bicarbonate. Na+ and water movement follows through the paracellular pathways. Na+ movement occurs through claudin-2, a protein of the junctional complex. Expression of claudin-2 is affected in the NKCC1-DFX and NKCC1 knockout mice. The tight junction protein is only observed at the base of the crypt and no longer observed at the epithelial cells along the side of the crypt.90