Figure 5.
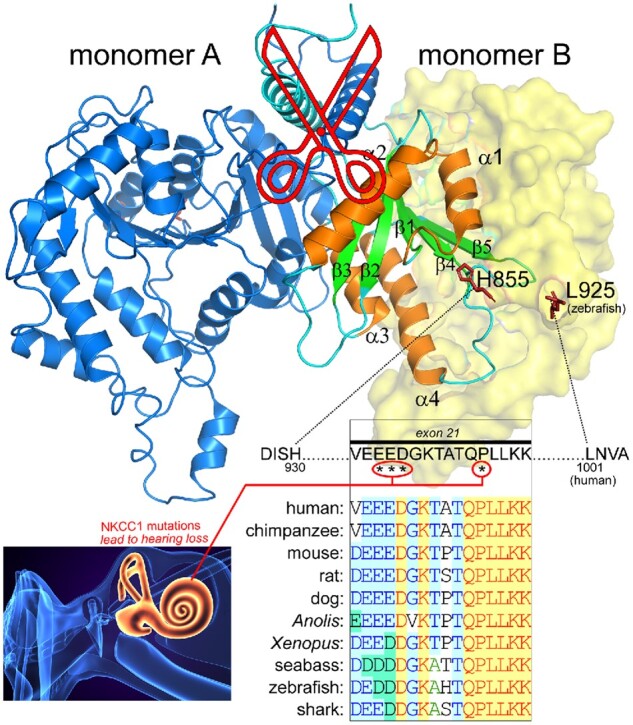
Structure of the Carboxyl-Terminus of NKCC1 Highlighting the Absence of a Peptide Containing Exon 21. Note that monomer A sits under the transmembrane core of monomer B and vice versa, with two helices crossing in scissor shape. The α-helices 1–4 and β-sheet 1–5 of monomer B are highlighted in orange and green colors, respectively. Residues between His855 and L925 (zebrafish) were nor resolved and therefore missing from the structure. Note that they are oriented in opposite directions in the two monomers making them unlikely to interact. The 69 stretch of missing residues in the structure includes the 16 amino acid encoded by exon 21. Four residues in this exon (human sequence, labeled by stars), including those creating an acidic motif, are involved in loss of hearing. These residues are highly conserved among vertebrate species. The D. rerio (zebrafish) NKCC1 structure26 was drawn using Pymol Molecular Graphic System (version 2.3.1, Schrodinger). The sequence alignment was created using VectorNti (version 6, Informax).
