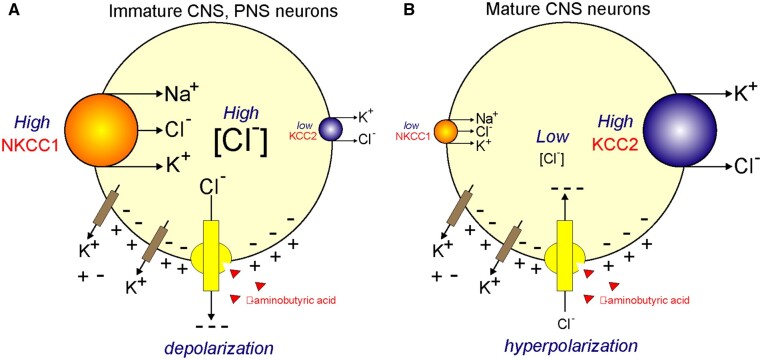
Figure 6.
Regulation of Intracellular [Cl−] in Neurons and Effect on GABA Receptor Function. (A) In immature central nervous system (CNS) neurons and in peripheral nervous system (PNS) neurons, the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter, NKCC1, is highly expressed, whereas the K-Cl cotransporter, KCC2, is minimally expressed (as in the CNS) or not expressed (as in the PNS). The activity of NKCC1 results in accumulation of intracellular Cl−. [Cl−] values range from 30 to 60 mM. As GABA binds to its receptor (GABAAR), it triggers the opening of a Cl− conductance and Cl− follows its electrochemical driving force leaving the cell and leading to depolarization of the neuronal membrane. The membrane potential is created by the leak of K+ through specific K+ channels. (B) In mature CNS neurons, NKCC1 expression or activity is low whereas expression and activity of KCC2 high. This results into low intracellular Cl− concentrations (<10 mM). When GABA binds, Cl− enters the cell and hyperpolarizes the membrane.