Figure 1.
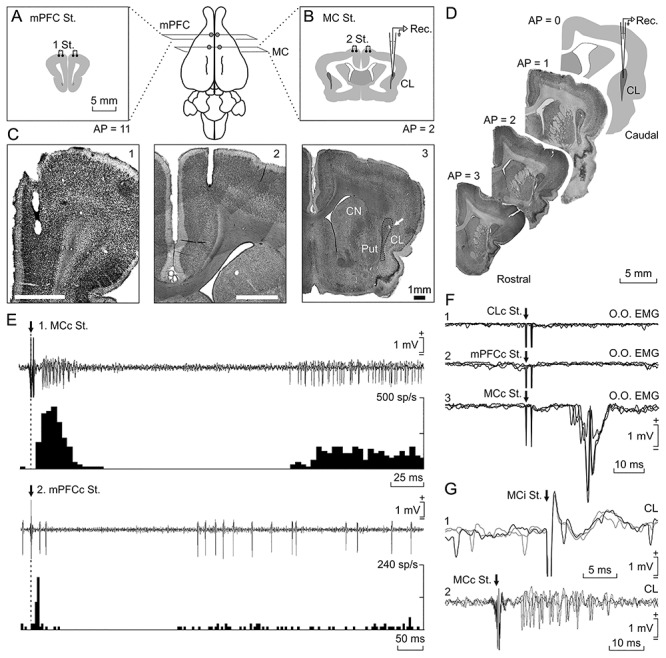
Location and identification of recorded neurons. Rabbits were bilaterally implanted with chronic stimulating electrodes in mPFC (A), M1 subdivision of MC (B), and CC (not illustrated). (C) Photomicrographs of coronal sections illustrating the location of stimulating electrodes in mPFC (1) and M1 (2). In (3), a microlesion in the dorsal CL is illustrated (arrow); it was carried out with a metal electrode implanted in a selected recording area; CN, caudate nucleus; Put, putamen. (D) Diagram of recording sites and images from targeted CL in four anteroposterior sections. The activity of CL neurons was recorded with glass micropipettes from rostral and central parts of the right dorsal CL (dotted line). Drawings in A, B, and D follow the atlas of Girgis and Shih-Chang (1981). (E) Three overlapped recordings illustrating short- and long-term synaptic activation of a CL neuron activated from the contralateral MC (1) and another one activated from the contralateral mPFC (2). Below each one is illustrated the peristimulus time histogram of 15 recordings. (F) From top to bottom are illustrated the EMG activity evoked in the left O.O. muscle by double pulses (2 ms interval) applied to the contralateral CL (1), mPFC (2), and MC (3). (G) Three overlapped recordings illustrating a CL neuron antidromically activated from the ipsilateral MC during the spike-triggered collision test (1). (2) illustrates the synaptic activation of a representative CL neuron from the contralateral MC.
