Figure 7.
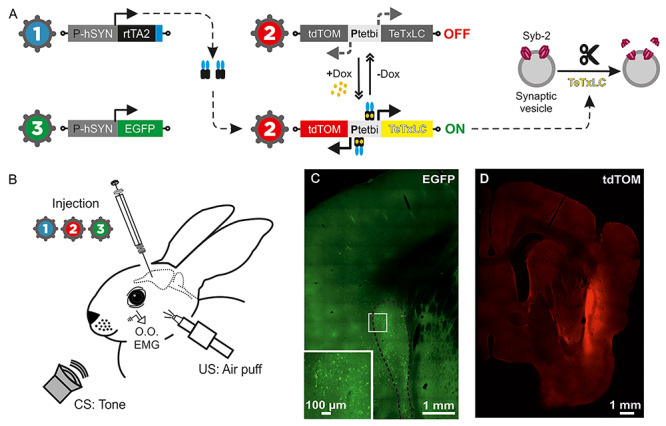
Animal preparation for classical eyeblink conditioning following virus-delivered inducible silencing of synaptic transmission (vINSIST) of CL neurons. (A) The three injected viruses were as follows: (1) rAAV–PhSYN–rtTA; (2) rAAV–Ptetbi–TeTxLC/tdTOM; and (3) rAAV–PhSYN–EGFP. With the vINSIST method, the reverse tetracycline trans activator (rtTA) is expressed under a human synapsin specific promoter (PhSYN) and the tetanus toxin light chain (TeTxLC) and tdTomato (tdTOM) are under a bidirectional tet responder promoter (Ptetbi). Only under doxycycline (Dox) treatment, rtTA binds the Ptetbi to express simultaneously TeTxLC, which blocks synaptic transmission, and tdTOM, a tracer that we used to identify the inhibited zone. Virus 3 acted as a post hoc histological tracer for validating the degree of precision and the expression of rtTA. (B) Diagram illustrating the animal’s injections with the rAAVs and its preparation for the classical conditioning of eyelid responses. (C) Photomicrographs from CL infected neurons glowing green due to EGFP fluorescent protein generated by the administered virus 3. The large white square is an amplification of the smaller one. (D) Photomicrograph from the inhibited CL glowing red due to tdTOM fluorescent protein generated by the activation of the Ptetbi by dox administration.
