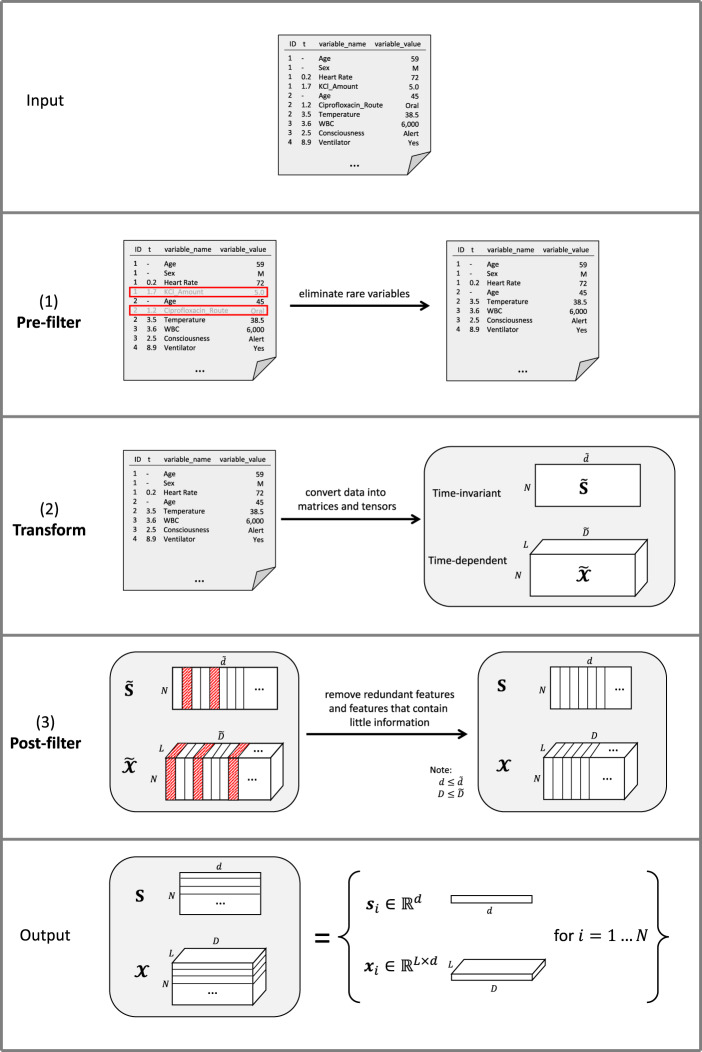
Figure 1.
Overview of FIDDLE. Given formatted input data and user-defined arguments, FIDDLE processes data in 3 stages: (1) pre-filter, (2) transform, and (3) post-filter. So long as the units are consistent, timestamps in the t column may be recorded at any level of granularity (eg, seconds, minutes, hours, days, visits, etc.). In this sample input file, we consider time in hours. A row with [1, 0.2, Heart Rate, 72] corresponds to a patient with ID = 1 with a heart rate = 72 bpm recorded at t = 0.2 h. In (1) pre-filter, FIDDLE eliminates rare variables. In (2) transform, FIDDLE transforms data into tensors containing time-invariant and time-dependent features. In (3) post-filter, FIDDLE removes redundant features and features that are likely uninformative. The output consists of binary vectors and , describing the features for each ID. bpm: beats per minute; FIDDLE: Flexible Data-Driven Pipeline: ID: unique identifier; KCl: potassium chloride; WBC: white blood cell.