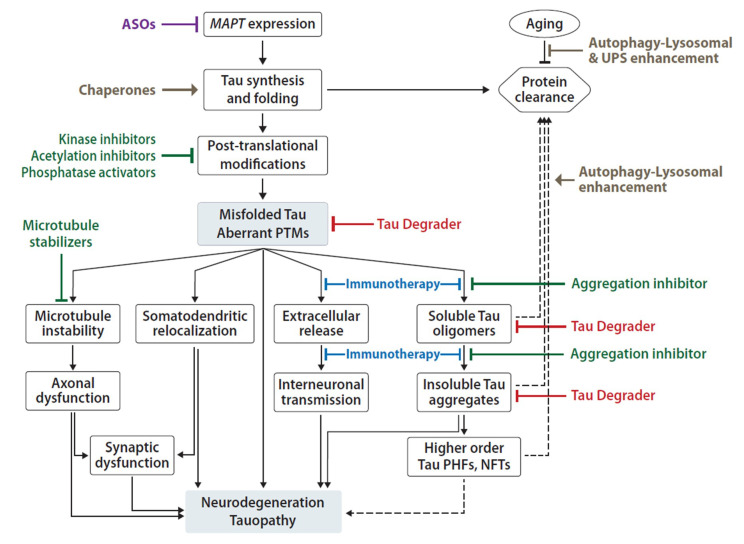
Figure 2.
Summary of proposed mechanisms of Tau pathogenicity and corresponding experimental therapeutic approaches. Tau toxicity can be driven by loss-of-function leading to microtubule depolymerization and axonal transport disruption; and it can be driven by gain-of-function of aberrant Tau oligomers, aggregates and fibrils associated with neuronal toxicity, pathology spread and ultimately death. Current development of therapeutic agents include reduction of MAPT expression by ASOs (purple), small molecule (green) inhibitors of PTMs and aggregation, enhancement of Tau folding and/or clearance mechanisms (brown), Tau-specific degraders (red) and anti-Tau immunotherapies (blue). Solid arrows represent known and/or direct effects; dashed arrows represent indirect/proposed mechanisms; flat-ended connections represent inhibitory effect.