Fig 1. Schematic presentation of the measurement of the investigated echocardiographic measures.
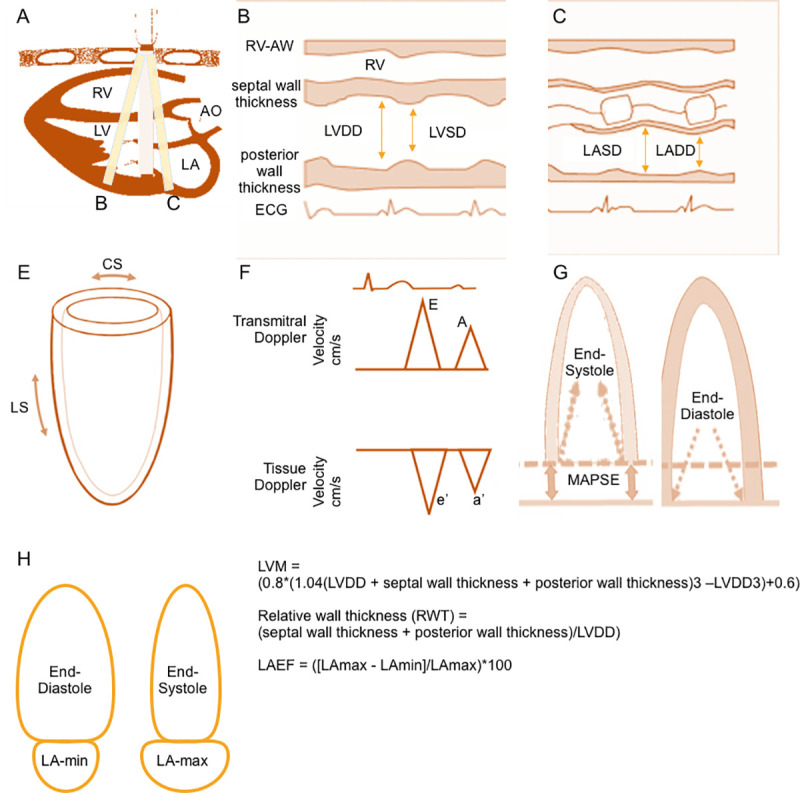
Panel A shows a 2D parasternal long axis view, lines B and C indicate the position of the m-mode. The respective m-mode view is shown in panels B and C. Left ventricular end-diastolic dimension (LVDD) and left ventricular end-systolic dimension (LVSD), posterior wall thickness, and septal wall thickness are measured as shown in panel B. Left ventricular mass (LVM), relative wall thickness (RWT) and left ventricular ejection fraction (LVEF) are calculated based on these measures. Left atrial end-systolic dimension (LASD) and left atrial end-diastolic dimension (LADD) are measured as shown in panel C. Panel E depicts the basic directions in which circumferential strain (CS) and longitudinal strain (LS) are measured. Panel F shows the measurements of transmitral Doppler (E and A) and tissue Doppler (e’ and a’) velocities. We have measured early systolic mitral annulus velocity using tissue Doppler imaging at the lateral mitral annulus. E/e’ ratio is calculated based on these measurements. Mitral annular plane systolic excursion (MAPSE) was measured by the systolic excursion of the mitral annulus from its lowest point at end-diastole (panel G, right) to its highest point at the time of aortic valve closure (panel G, left) at the lateral side of the mitral valve annulus in the apical four-chamber view. Maximum and minimum volumetric measurements of the LA (LAmax and LAmin) from apical two and four-chamber views were taken at end-diastole for LAmin (panel H, left) and at end-systole for LAmax (panel H, right). Left atrial emptying fraction (LAEF) is calculated based on these measurements.
