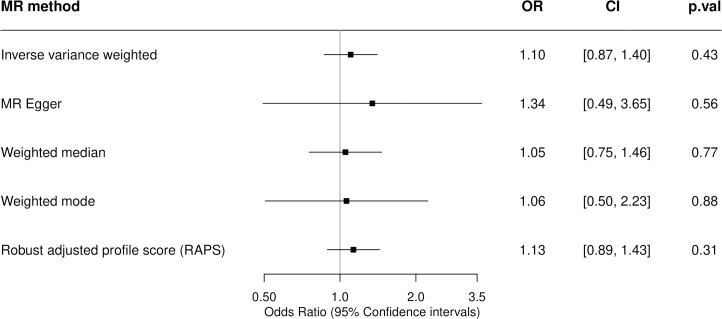
Fig 3. Two-sample MR estimates of the association between lifetime smoking and the incidence of MS.
A two-sample MR analysis was undertaken to obtain causal estimates of genetically predicted lifetime smoking on MS susceptibility. MR and sensitivity analyses were performed using the TwoSampleMR R package with a comparison across 5 different methods. ORs are expressed per 1 SD increase of the lifetime smoking index. A SD increase in the lifetime smoking score is equivalent to an individual smoking 20 cigarettes a day for 15 years and stopping 17 years ago or an individual smoking 60 cigarettes a day for 13 years and stopping 22 years ago. The genetic variants used to proxy lifetime smoking are the independent genome-wide significant SNPs taken from the GWAS of lifetime smoking performed by Wootton and colleagues detailed in Table C in S1 Data. The estimates of their association with MS are taken from the 2019 MS Chip IMSGC meta-analysis. CI, confidence interval; GWAS, genome-wide association study; IMSGC, International Multiple Sclerosis Genetics Consortium; MR, Mendelian randomization; MS, multiple sclerosis; OR, odds ratio; p.val, p-value; RAPS, robust adjusted profile score; SD, standard deviation; SNP, single nucleotide polymorphism.