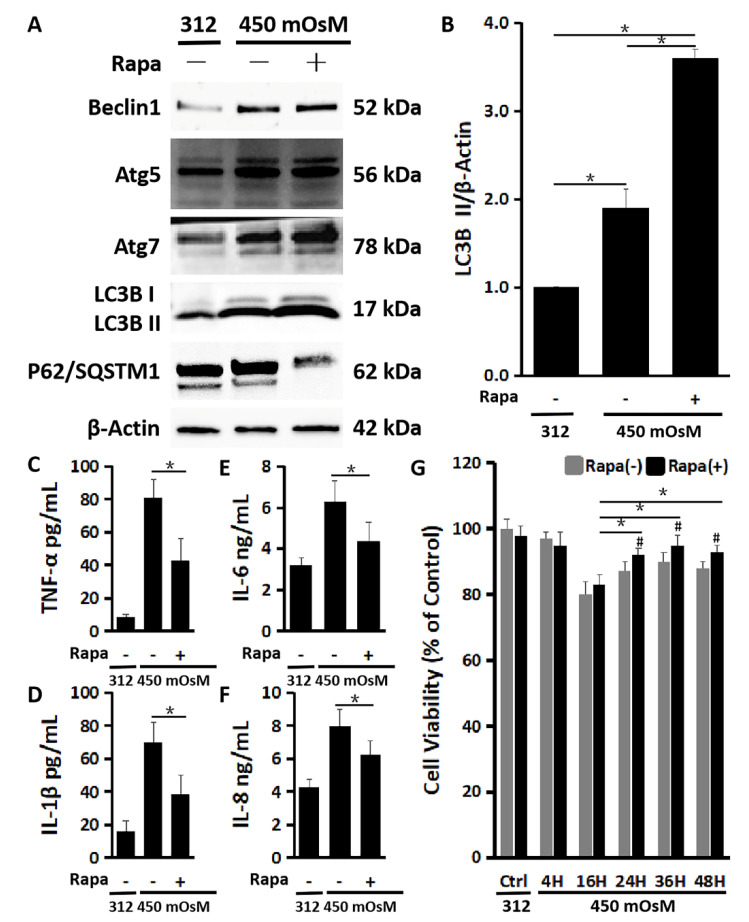
Figure 4.
Rapamycin enhanced autophagy activation and protected the cells from inflammation and reduced viability in primary HCECs exposed to hyperosmolarity. (A) Western blot showed that 200 nM of rapamycin increased production of Beclin1, Atg5, Atg7 and LC3B while it decreased p62 production in HCECs exposed to 450 mOsM for 2 h, with β-Actin as internal control. (B) Quantitative analysis of relative turnover levels of LC3B II/β-Actin. (C–F) ELISA results showed that the release of TNF-α (C), IL-1β (D), IL-6 (E) and IL-8 (F) were reduced by 200 nM of rapamycin in HCECs exposed to 450 mOsM medium for 2 h. (G) MTT assay showed that the cell viability was largely rescued by rapamycin after 24 h in HCECs exposed to 450 mOsM medium when compared with cell viability in normal medium (312 mOsM) at 24 h as controls. Data are presented as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. * p < 0.05, compared between two groups. # p < 0.05, compared within the same time point.