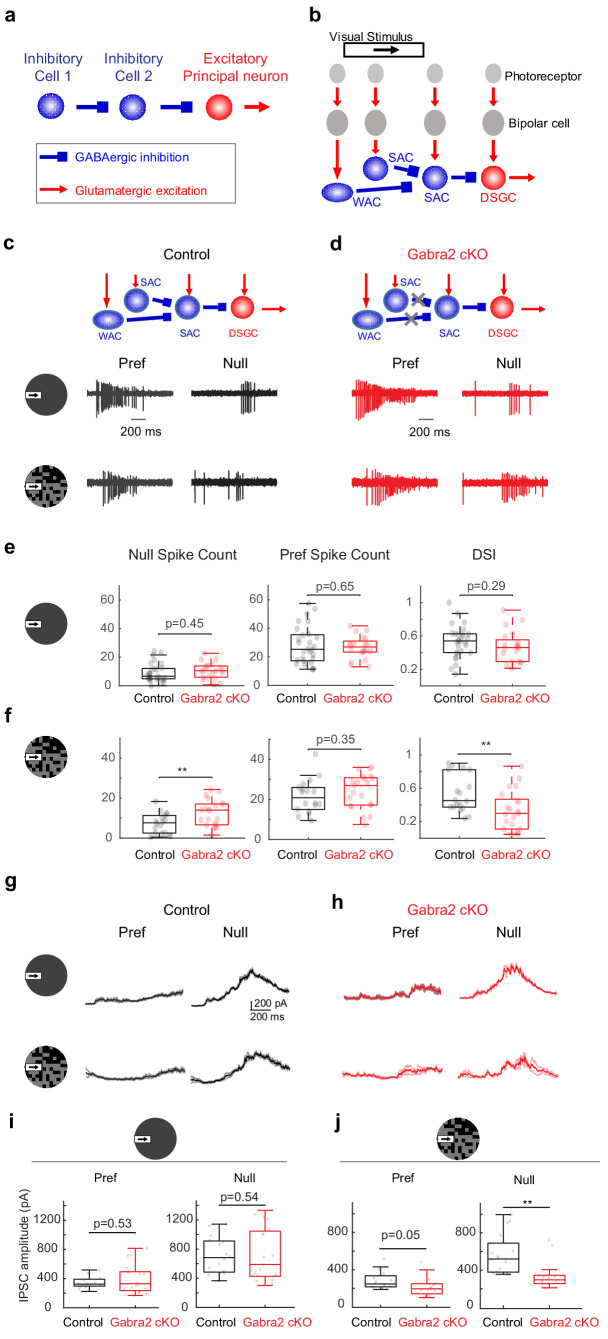
Figure 1. On-Off DSGCs in Gabra2 cKO mice show reduced direction selectivity and reduced null-direction inhibition in the noisy background.
(a) Organization of a canonical disinhibitory microcircuit. (b) Schematic of disinhibitory motifs WAC-SAC-DSGC and SAC-SAC-DSGC in the direction-selective circuit. WAC, SAC, and DSGC receive light-evoked glutamatergic inputs from the photoreceptor-bipolar cell signaling pathway. DSGC axons leave the retina and innervate higher brain nuclei. (c-f) DSGC spiking activity (c) Upper: schematic of disinhibitory motifs in control mice. Lower: example spiking activity of a DSGC in the control group during a moving bar in the preferred (pref) and null directions in noise-free (upper traces) and noisy (lower traces) backgrounds. (d) Same as c, from a DSGC in the Gabra2 cKO group. (e) Summary plots of null-direction (left), preferred-direction (middle) spike counts and direction selectivity index (DSI, see Materials and methods) in control and Gabra2 cKO groups for moving bar in the noise-free background. Box plots represent minimum / first quartile / median / third quartile / maximum values for this and subsequent figures, dots represent individual cells. Control: n = 19 cells from 6 mice. Gabra2 cKO: n = 20 cells from 6 mice. (f) Same as (e) for moving bar in the noisy background. (g-j) DSGC IPSC . (g) Example bar-evoked IPSC traces of a DSGC in the control group during a moving bar in the preferred and null directions in noise-free (upper traces) and noisy (lower traces) backgrounds. Three individual trials (thin lines) and the mean (thick line) are shown. (h) Same as g, from a DSGC in Gabra2 cKO group. (i) Summary plots of preferred- (left) and null-direction (right) IPSC peak amplitudes in control and Gabra2 cKO groups for moving bar in the noise-free background. Control: n = 17 cells from 6 mice. Gabra2 cKO: n = 20 cells from 7 mice. (j) Same as I, for moving bar in the noisy background. See also Figure 1—figure supplements 1–3.