Figure 4. Interrelationship between astrogliosis and cerebrovascular dysfunction.
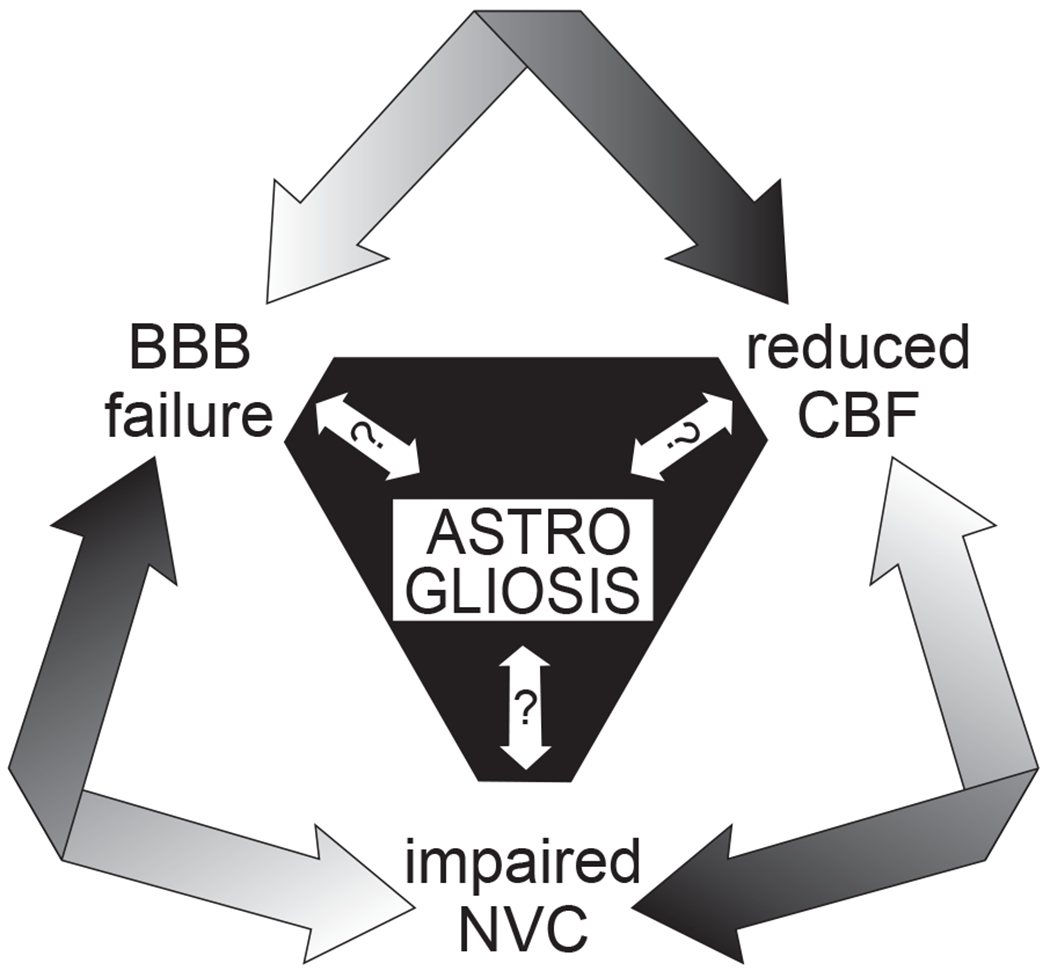
Do reactive astrocytes contribute to pathological cerebrovascular dysfunction in disease? With their central positioning between neurons and cerebral vessels and their multifaceted roles in homeostatic blood-brain barrier (BBB) maintenance, cerebral blood flow (CBF) regulation, and neurovascular coupling (NVC), astrocytes have the potential to adversely affect all of these processes when they are reactive and in a morphologically and functionally altered state. Although astrogliosis almost certainly contributes to and exacerbates the dysfunction of these processes, it is unclear whether it precedes them or results from them.
