Figure 4. Endoplasmic reticulum stress-induced kinases:
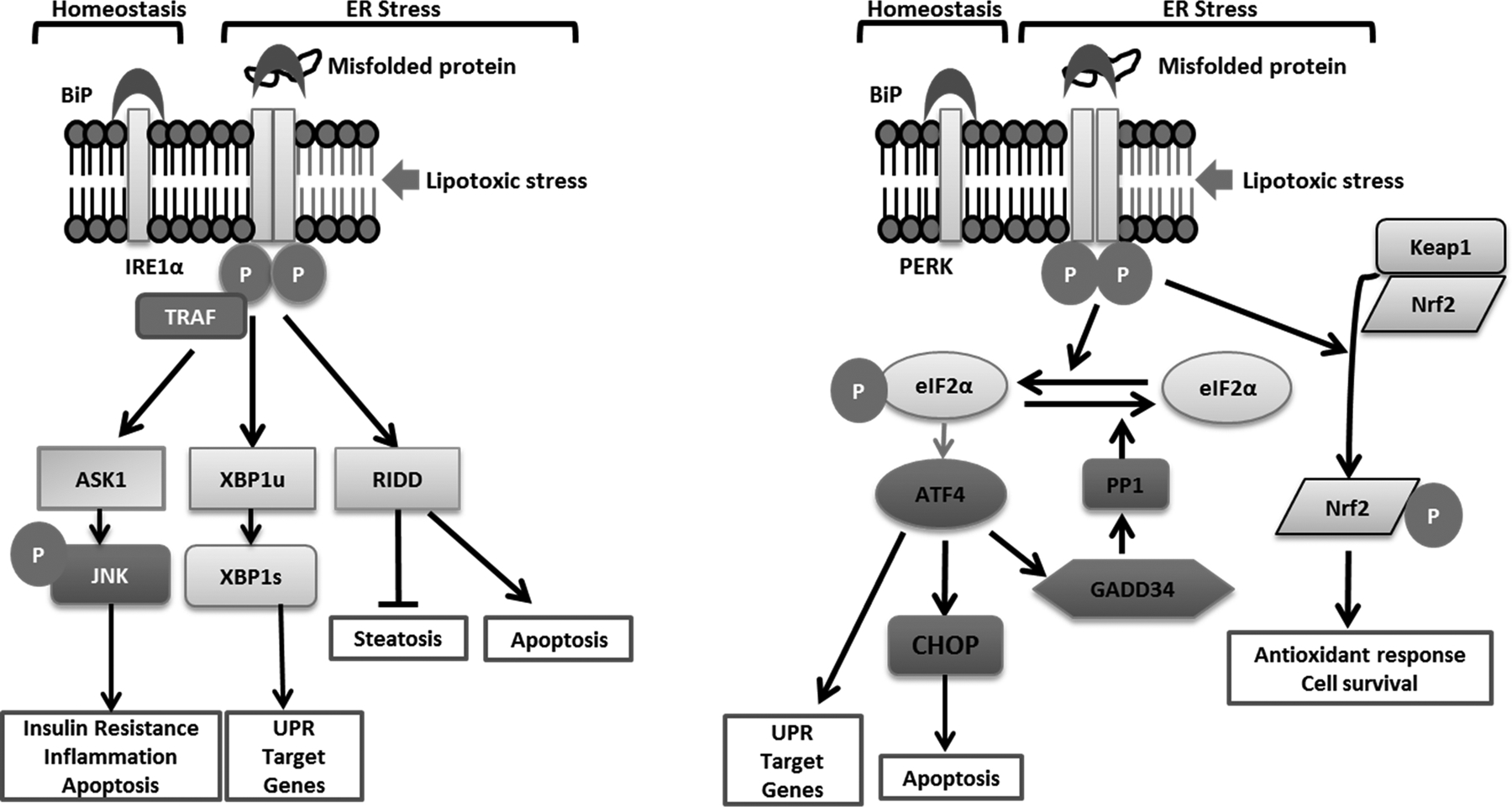
IRE1α and PERK signaling under homeostatic conditions is kept in check by inhibitory binding of their respective luminal domains to BiP. Proteotoxic ER stress due to the accumulation of misfolded proteins in the ER lumen dissociates BiP from the luminal domains allowing oligomerization-induced activation. Lipotoxic stress-induced oligomerization occurs independent of the luminal domains of IRE1α and PERK. The sensing mechanisms for proteotoxic and lipotoxic stress appear to be conserved between IRE1α and PERK. IRE1α-induced oligomerization by TRAF2 activates a kinase cascade resulting in activation of ASK1 and JNK. JNK is implicated in insulin resistance, inflammation and apoptosis. Activation of the kinase domain of IRE1α results in trans-autophosphorylation and activation of the cytosolic endoribonuclease (RNase) activity which cleaves 26 nucleotides from XBP1 mRNA to express spliced XBP1. XBP1 is a potent transcription factor upregulating a program of UPR target genes including the chaperone BiP. IRE1α also cleaves mRNAs and microRNAs in a process termed regulated IRE1α-dependent decay (RIDD). RIDD targets inhibit steatosis and promote apoptosis. PERK phosphorylates eIF2α leading to attenuation of translation with selective translation of ATF4. ATF4 induce the expression of CHOP, which sensitizes cells to ER stress-induced apoptosis. ATF4 also activates an adaptive program of stress responsive UPR target genes such as amino acid metabolism. CHOP and ATF4 together increase the expression of GADD34, which activates protein phosphatase 1 (PP1). PP1 dephosphorylates eIF2α, removing the brakes on translation. PERK also phosphorylates Nrf2 leading to its dissociation from Keap1, which leads to its nuclear translocation and activation of Nrf2 target genes including antioxidant genes which favor cell survival.
