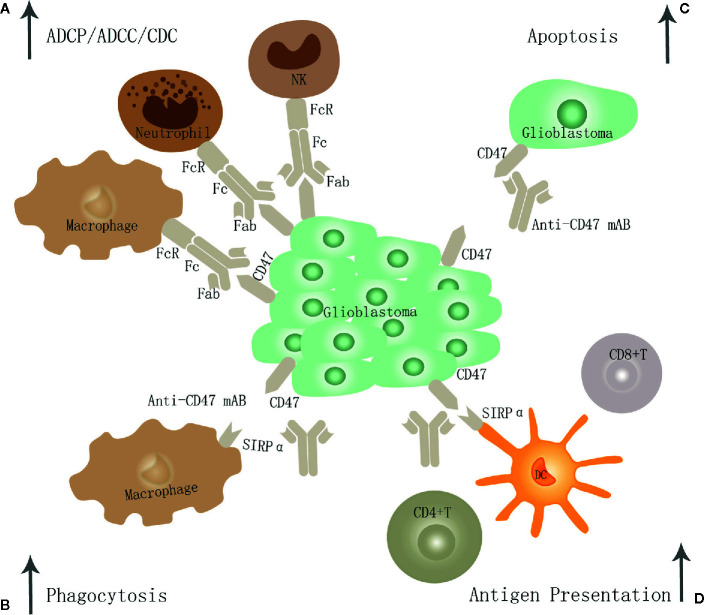
Figure 2.
The potential mechanism of CD47-SIRPα inhibition in GBM. Targeting the CD47-SIRPα axis may exert anti-GBM effects through the following four pathways: (A) Eliminate GBM cells through traditional antibody Fc-dependent mechanisms, including ADCP, ADCC, and CDC. (B) it leads to enhanced tumor cell phagocytosis by macrophage through disrupting the binding of CD47 to SIRPα. (C) Promote apoptosis of GBM cells. (D) Restore dendritic cells' function to present antigen to CD4+ and CD8+T cells, thereby stimulating an anti-tumor adaptive immune response.