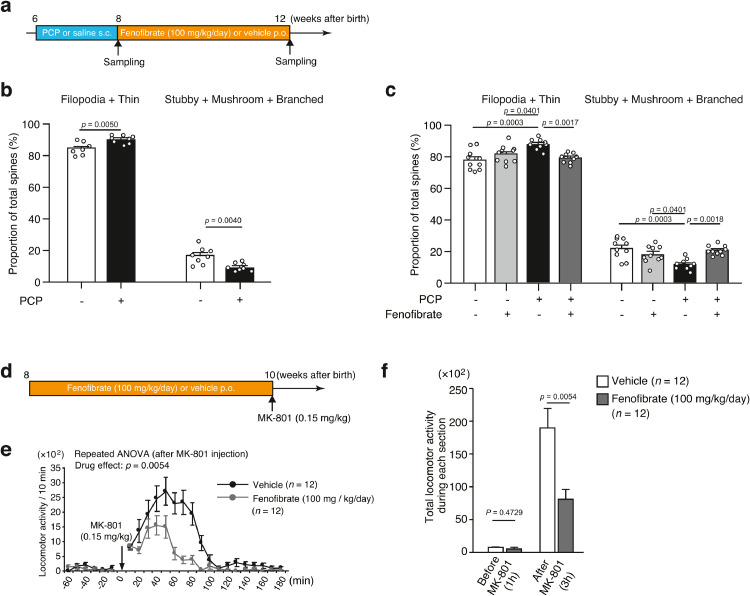
Fig. 6.
Effect of the PPARα agonist fenofibrate.
(a) Schedule of treatment with fenofibrate.
(b) Morphological classification of spines in saline-administered mice (4 mice, 8 cells) and phencyclidine (PCP)-administered mice (3 mice, 8 cells). The values represent the mean ± standard error. The data were analyzed using unpaired t-tests.
(c) Morphological classification of spines in saline/vehicle-administered mice (4 mice, 10 cells), saline/fenofibrate-administered mice (6 mice, 10 cells), PCP/vehicle-administered mice (4 mice, 10 cells), and PCP/fenofibrate-administered mice (5 mice, 10 cells). The values represent the mean ± standard error. The data were analyzed using one-way ANOVA (p < 0.001), followed by Tukey's test.
(d) Experimental design for the MK-801-induced locomotor hyperactivity test following chronic administration of fenofibrate.
(e) Locomotor activity before and after a single injection of MK-801 (0.15 mg/kg body weight). The values represent the mean ± standard error. The data were analyzed using two-way repeated-measures ANOVA (drug effect, p < 0.001).
(f) Cumulative locomotor activity before and after MK-801 injection. The values represent the mean ± standard error. The data were analyzed using unpaired t-tests.