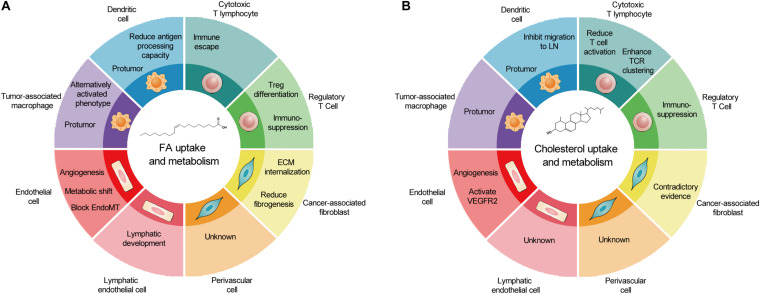
FIGURE 2.
The outcomes of fatty acid and cholesterol metabolism in cancer-associated host cells. (A) In TME, FA metabolism promotes metabolic shift and angiogenesis in EC and LEC, reduces fibrogenesis, and generally induces protumor phenotype in immune cells. (B) In contrast, cholesterol metabolism promotes EC proliferation, induces protumor phenotype in immune cells, and produces contradictory effects in CAFs and cytotoxic T lymphocytes. Of note, several host cell types remain un-investigated. TME, tumor microenvironment; FA, fatty acid; EC, endothelial cell; LEC, lymphatic endothelial cell; CAFs, cancer-associated fibroblasts.